Massive Solar Filament Erupts, Displaying Sun's Power, But Earth Spared
On May 7, 2025, a substantial solar filament erupted from the sun. While the eruption was visually stunning, it was directed away from Earth, preventing any direct impact. Forecasters are monitoring space weather events that could trigger auroras at high latitudes.

 Space
Space
NASA Combines Telescopic Data to Create 3D Models of Supernova Remnants
NASA has created 3D models of cosmic objects, including supernova remnants like Cassiopeia A, G292.0+1.8, Cygnus Loop, and the young star BP Tau, using data from Chandra X-ray Observatory and other telescopes. These models, some 3D-printable, offer new ways for students, educators, and the visually impaired to study these celestial structures, providing insight into star evolution and supernova dynamics.
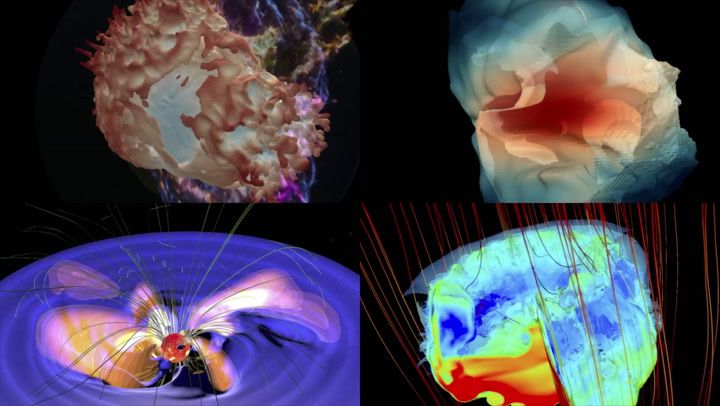
 Space
Space
 Phys.org
Phys.org
 3Dnatives
3Dnatives
 Wion
Wion
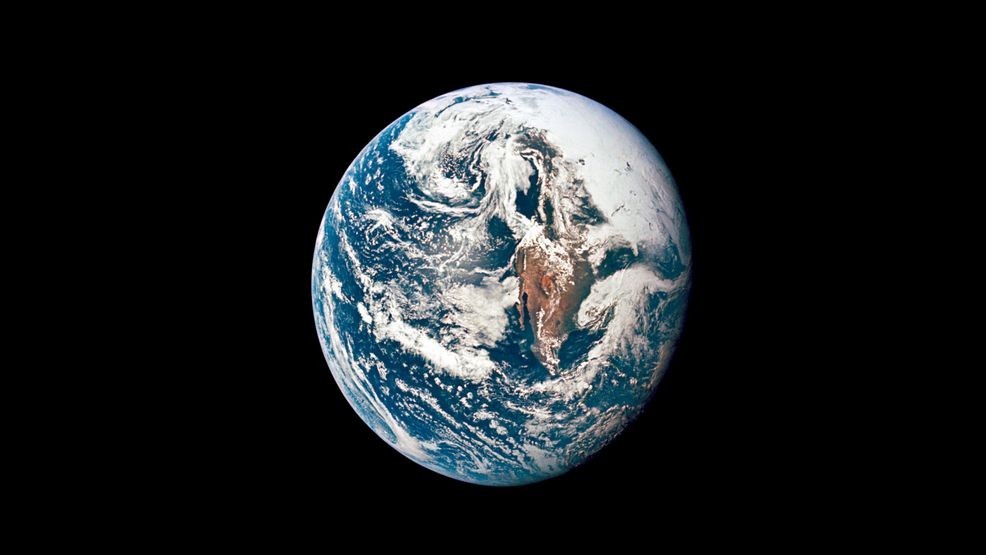
Earth's Oxygen to Vanish in a Billion Years, NASA-Led Study Predicts
A NASA-led study, in collaboration with Toho University, forecasts that Earth's oxygen will deplete in a billion years. The aging sun, growing hotter and more luminous, will disrupt the carbon cycle, diminishing plant life and oxygen production. This will lead to an atmosphere rich in methane, making complex life unsustainable, leaving only hardy microbes. Climate change is a short-term threat, while this is a long-term event.

 WKRC
WKRC
 BBC Sky at Night Magazine
BBC Sky at Night Magazine
 Hindustan Times
Hindustan Times
 Energy Live News
Energy Live News
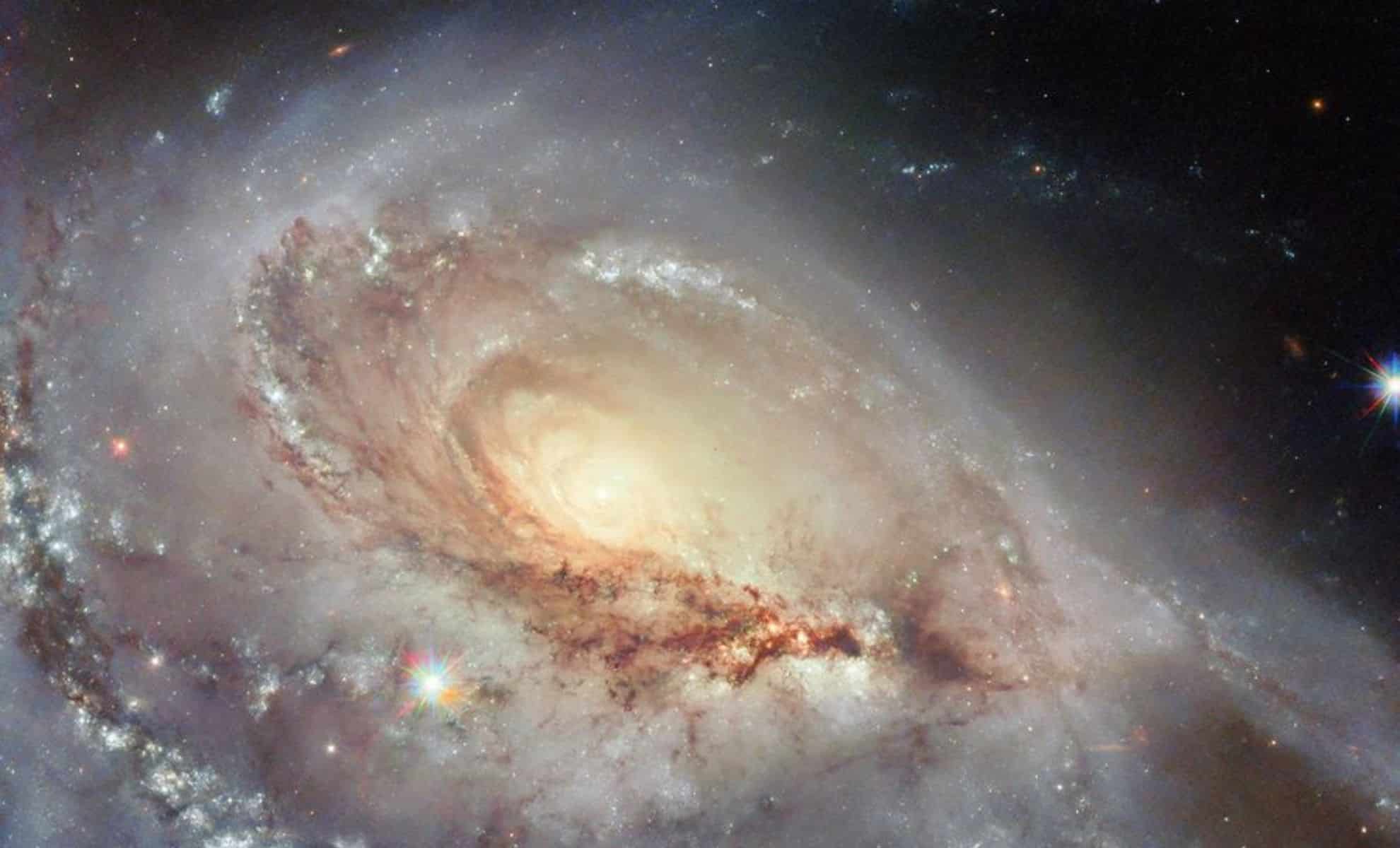
Hubble Captures Stunning Image of Peculiar Spiral Galaxy Arp 184 (NGC 1961)
The Hubble Space Telescope has released a striking image of Arp 184 (NGC 1961), a peculiar spiral galaxy notable for its asymmetrical structure featuring one prominent spiral arm. Located 190 million light-years away in the constellation Camelopardalis, Arp 184 is part of Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies and has hosted four supernovae in the last three decades, making it a subject of ongoing astronomical study.

 The Daily Galaxy
The Daily Galaxy
 NASA Science (.gov)
NASA Science (.gov)
 Space
Space
 PetaPixel
PetaPixel
Starlings Form Friendships Through Reciprocal Breeding Assistance, Study Reveals
A new study on superb starlings reveals that these birds engage in reciprocal helping behavior, offering assistance to unrelated flock members in raising chicks with the expectation of future reciprocation. This behavior, observed over 20 years, challenges the traditional understanding of altruism in cooperative breeding and suggests the formation of lasting social bonds, resembling friendships, among the birds.

 ScienceAlert
ScienceAlert
 The New York Times
The New York Times
 The Guardian
The Guardian
 New Scientist
New Scientist
China Achieves Daytime Laser Ranging to Moon, Advancing Deep Space Capabilities
China has achieved a significant milestone by conducting the first daytime laser-ranging test between Earth and the moon. The experiment, involving the Tiandu-1 satellite, demonstrates China's enhanced capabilities in deep-space communication and navigation. This breakthrough has implications for future lunar missions, including the International Lunar Research Station, and highlights China's growing role in space exploration.

 Space
Space
 Sustainability Times
Sustainability Times
 IFLScience
IFLScience
 China Daily
China Daily
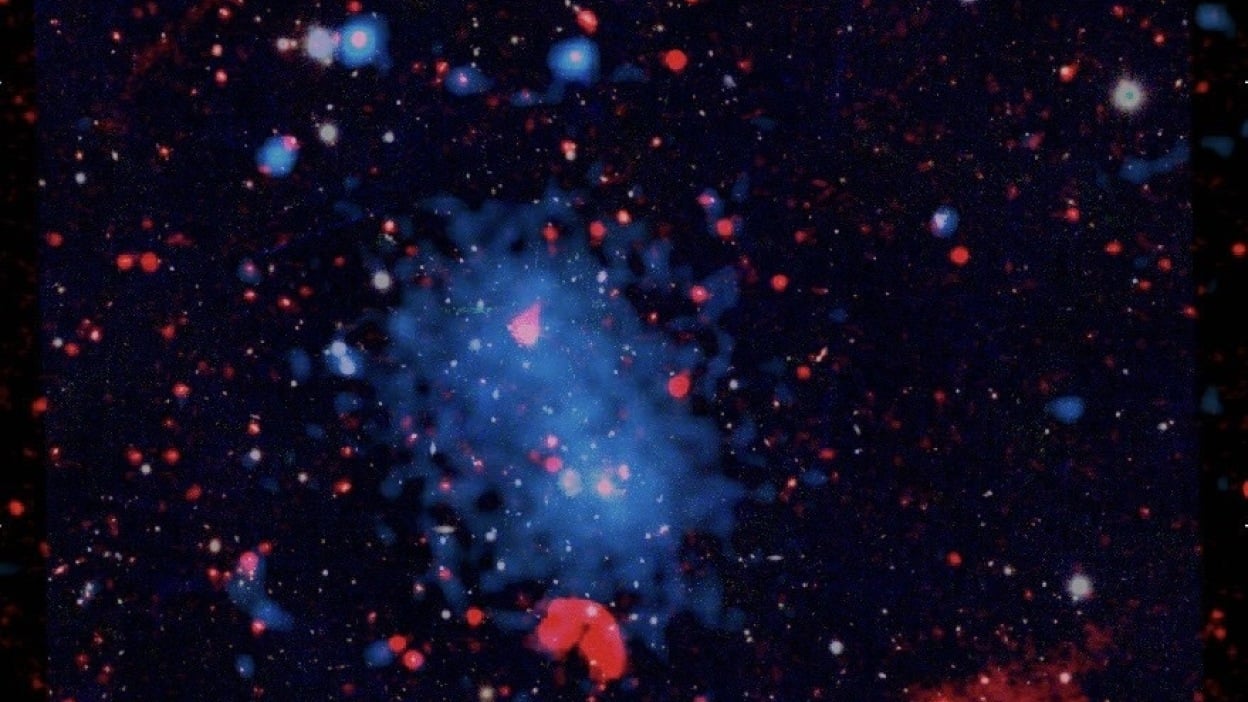
Rare Radio Relics Discovered in Galaxy Cluster Nearly a Billion Light-Years Away
Astronomers have discovered a pair of radio relics in galaxy cluster PSZ2 G181.06+48.47, located approximately 963 million light-years from Earth. These relics, formed by shockwaves from a collision between two galaxy groups, span 11 million light-years, making them the largest known. The discovery provides insights into galaxy cluster mergers and the formation of radio halos.

 Mashable
Mashable
Muscle Function Resilient Despite Significant NAD Depletion, Challenging Anti-Aging Hype
A recent study challenges the widely accepted role of NAD in muscle health and aging. Researchers found that significant NAD depletion in mice skeletal muscles did not impair muscle function, exercise capacity, or accelerate aging. This research questions the effectiveness of NAD-boosting supplements and calls for a re-evaluation of NAD's role in energy metabolism and age-related decline.

 bestlifeonline.com
bestlifeonline.com
 BioWorld MedTech
BioWorld MedTech
 Medical Xpress
Medical Xpress
 ScienceBlog.com
ScienceBlog.com
Deep-Sea Polymetallic Nodules: A Novel Oxygen Source and Implications for Extraterrestrial Life
Scientists have discovered that polymetallic nodules in the deep ocean can produce oxygen through electrochemical reactions, independent of photosynthesis. This finding challenges existing understanding of oxygen production and has significant implications for understanding the origins of life on Earth and the potential for life on other planets, especially oceanic moons like Europa. Further research is planned to investigate these nodules.

 Farmingdale Observer
Farmingdale Observer
Molecular Duo: Protein Bond Offers Clues to Long-Lasting Memory Storage
A new study suggests a protein bond between PKMζ and KIBRA plays a vital role in maintaining long-term memories, addressing the paradox of fleeting molecules forming enduring memories. Researchers found this interaction strengthens synapses and persists over time, allowing for molecular replacement without disrupting memory. The discovery offers insight into how memories withstand molecular turnover.

 Quanta Magazine
Quanta Magazine
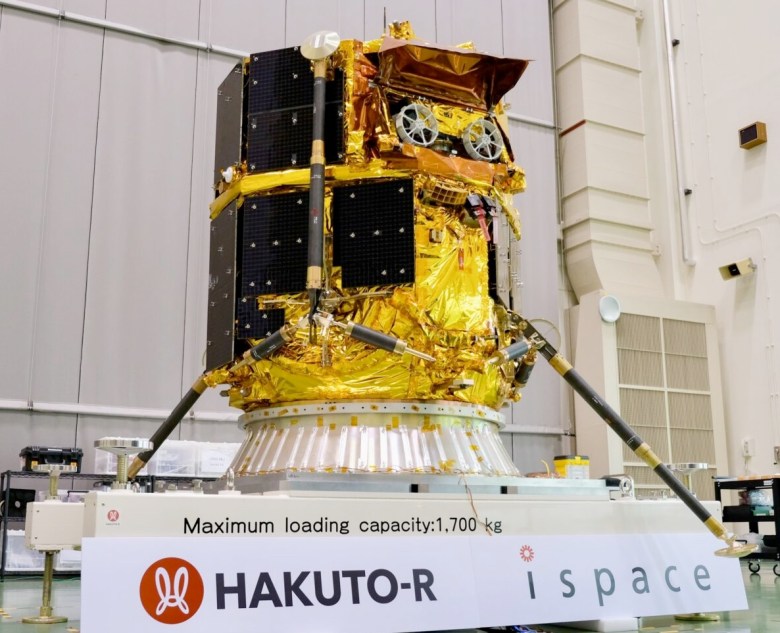
Ispace's Resilience Lunar Lander Enters Orbit, Aims for June Touchdown
Ispace's Resilience lander has entered lunar orbit, setting the stage for a landing attempt in early June. This mission follows a previous failed landing in 2023. The lander carries various payloads, including a mini rover and technology demonstration experiments. The success of this mission would mark a significant achievement for private lunar exploration.

 NBC News
NBC News
 SpaceNews
SpaceNews
 The Japan Times
The Japan Times
 Space
Space
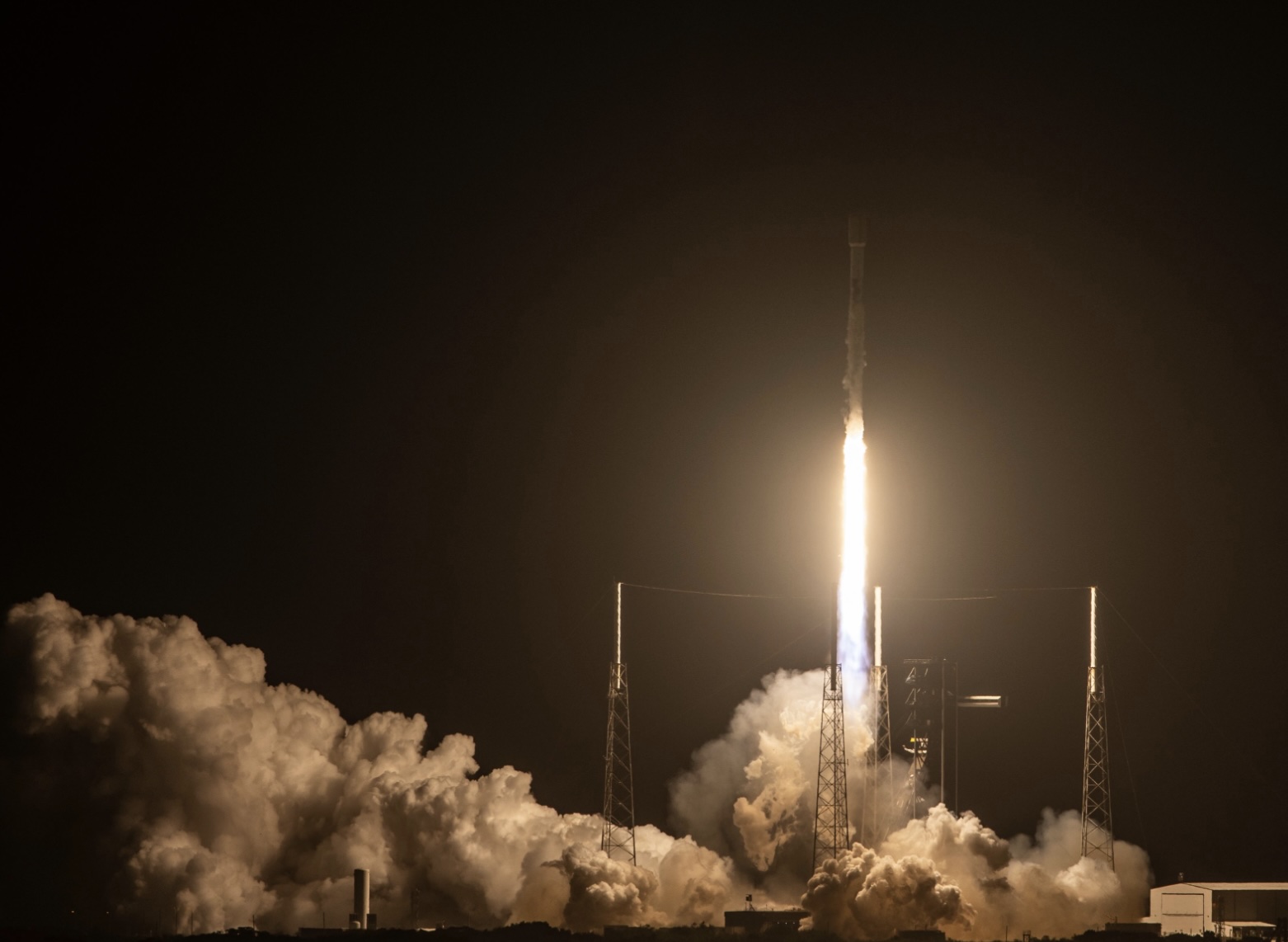
SpaceX Expands Starlink with Falcon 9 Launch Amid Surging Global Demand
SpaceX launched a Falcon 9 rocket carrying Starlink satellites to expand its constellation, now exceeding 7,300 satellites. The launch occurred from Cape Canaveral, Florida. This expansion aims to meet the surging global demand for satellite internet connectivity, highlighted by Starlink's crucial role during a recent blackout in Spain and Portugal and amidst growing competition from Amazon's Project Kuiper and other initiatives.

 Teslarati
Teslarati
 Yahoo
Yahoo
 KSBY News
KSBY News
 Spaceflight Now
Spaceflight Now
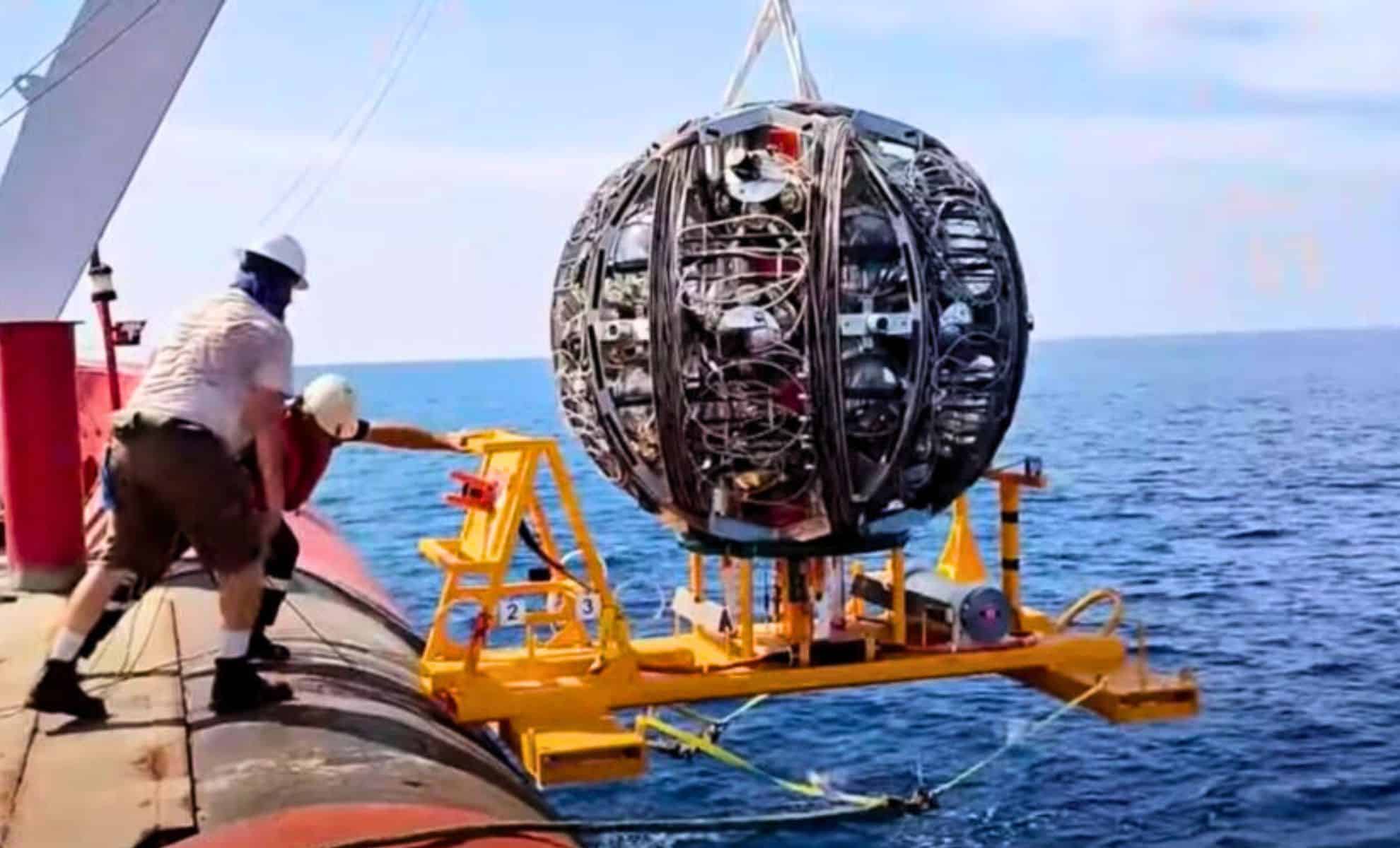
Record-Breaking Neutrino Detected in Mediterranean Sea, Shedding Light on Universe's Mysteries
Scientists have detected a neutrino with unprecedented energy using the KM3NeT telescope, a deep-sea observatory off the coast of Sicily. The discovery, made in February 2023, offers a new window into extreme astrophysical phenomena and could help unlock mysteries about the origins of ultra-high-energy cosmic particles, such as black holes and supernovas. Further research aims to pinpoint the neutrino's source and understand its significance.

 The Daily Galaxy
The Daily Galaxy
 New Scientist
New Scientist
 CORDIS
CORDIS
 Sciworthy
Sciworthy
Deep-Sea Telescope Detects Highest-Energy Neutrino, Unveiling Cosmic Mysteries
Scientists have detected the highest-energy neutrino ever observed using the KM3NeT telescope in the Mediterranean Sea. This groundbreaking discovery, supported by EU-funded projects, provides a new window into extreme astrophysical phenomena like exploding stars and black holes. The neutrino's energy far exceeds previous detections, opening possibilities for understanding the universe's most energetic events.

 The Daily Galaxy
The Daily Galaxy
 New Scientist
New Scientist
 CORDIS
CORDIS
 Sciworthy
Sciworthy
Ispace's Resilience Lunar Lander Enters Orbit, Aims for June Touchdown
The Ispace Resilience lunar lander has successfully entered lunar orbit, marking a significant step toward a planned landing in early June. The mission, which launched in January, aims to land near Mare Frigoris and includes a mini rover for lunar surface exploration. This follows Ispace's previous failed landing attempt in 2023 and ongoing commercial lunar efforts.

 SpaceNews
SpaceNews
 NBC News
NBC News
 The Japan Times
The Japan Times
 Space
Space
Modern Animals with Dinosaur Traits: Chickens, Crocodiles, and More
This article identifies ten modern animals that possess physical and behavioral traits reminiscent of dinosaurs. It highlights shared characteristics such as armored skin, sharp claws, beaks, and hunting strategies, tracing evolutionary connections and showcasing how the dinosaur legacy persists in present-day fauna. Species include chickens, crocodiles, cassowaries and more.

 Times of India
Times of India
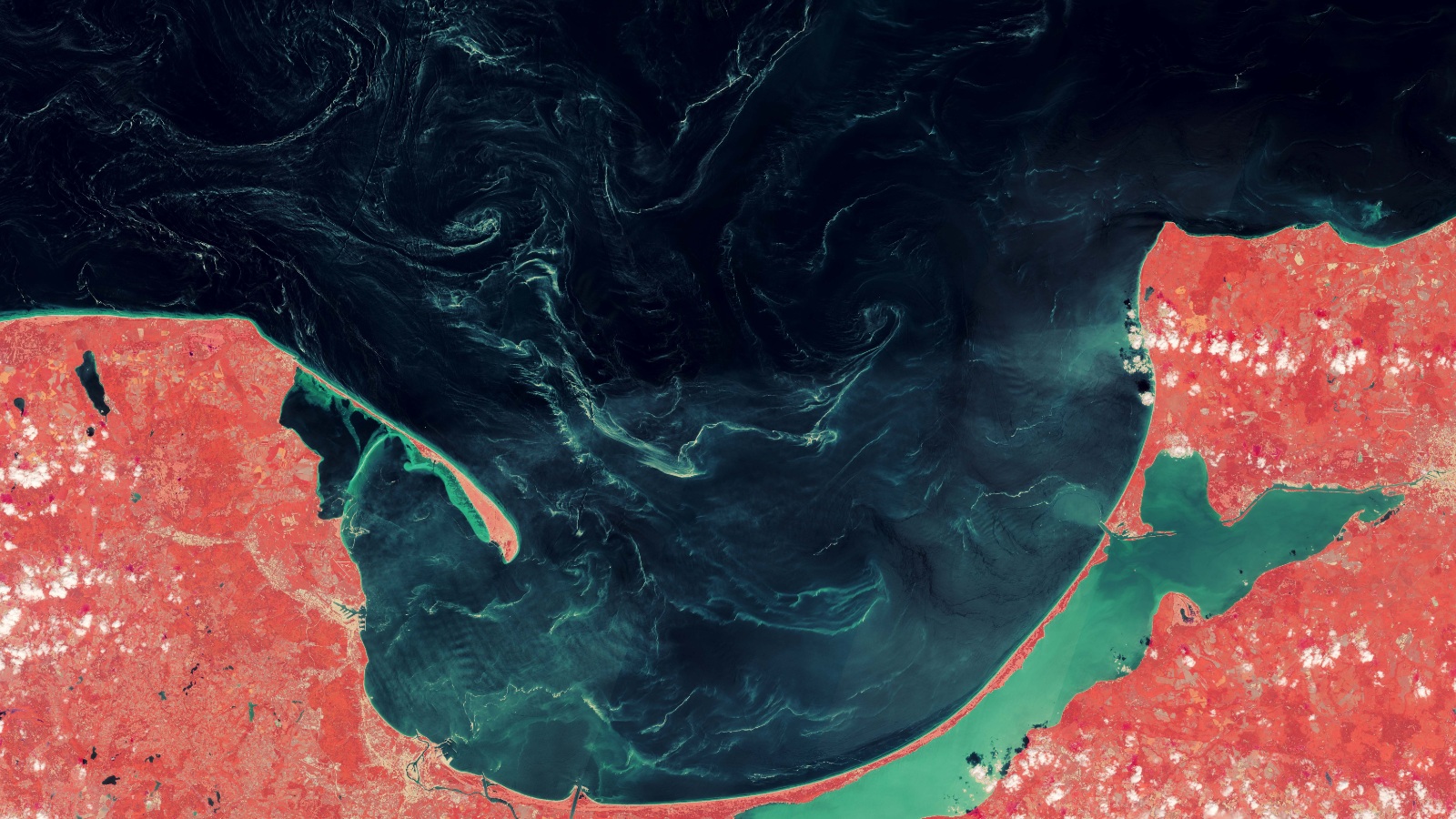
Baltic Sea's Mysterious Swirls Identified as Tree Pollen After Years of Uncertainty
Mysterious slicks appearing in the Gulf of Gdańsk, Baltic Sea, have been identified as tree pollen, specifically from pine trees. These slicks, which can extend over 130 miles, were initially of unknown composition until a 2023 study revealed their source. The discovery highlights the significant role of tree pollen in marine ecosystems and the potential impact of climate change on pollen levels.

 Live Science
Live Science
Magnetar Flares: New Clue to the Cosmic Origin of Gold, Heavy Elements
Recent research indicates that magnetar giant flares, powerful bursts of energy from highly magnetized neutron stars, may be a crucial source of heavy elements, including gold. This discovery addresses a long-standing mystery in astrophysics, offering a new perspective on how elements heavier than iron are formed and distributed throughout the universe, potentially impacting our understanding of the origins of life.

 Space
Space
 The Washington Post
The Washington Post
 The Advocate
The Advocate
 Al Jazeera
Al Jazeera
NASA, Universities Predict Earth's Oxygen Depletion in One Billion Years
Research indicates Earth's oxygen levels will decline in about one billion years as the aging Sun heats the planet, disrupting climate systems and weakening the carbon cycle. The atmosphere will revert to a state similar to early Earth, rich in methane and poor in oxygen, leading to the extinction of complex life. Scientists emphasize that while this is a long-term concern, climate change remains a pressing challenge.

 BBC Sky at Night Magazine
BBC Sky at Night Magazine
 WKRC
WKRC
 Energy Live News
Energy Live News
 MSN
MSN
ESA's Biomass Satellite: Antenna Deployment and Forest Carbon Mapping Advancements
The European Space Agency's Biomass mission achieved a critical milestone with the successful deployment of its 12-meter antenna. This mission aims to revolutionize forest carbon measurement using P-band radar. Concurrently, a new comprehensive dataset combining various satellite missions, offers detailed insights into global forest biomass and carbon storage trends, supporting climate modeling and forest management.

 European Space Agency
European Space Agency
 Earth.com
Earth.com
 Biomass Magazine
Biomass Magazine
 GovTech
GovTech









