Probiotics vs. Prebiotics: Understanding Their Roles in Gut Health
This article clarifies the distinction between probiotics and prebiotics, emphasizing their roles in maintaining a healthy microbiome. It highlights the importance of a diverse microbiome for overall health and discusses the effectiveness of probiotic and prebiotic supplements, while advocating for obtaining these nutrients through a balanced diet rich in fermented foods and plant-based fibers.

 The Conversation
The Conversation
Probiotics vs. Prebiotics: Understanding Their Role in Gut Health
This article clarifies the distinction between probiotics and prebiotics, explaining their functions and relationship to the gut microbiome. It highlights the importance of a diverse microbiome for overall health and suggests obtaining probiotics and prebiotics through a varied diet of fermented and plant-based foods, rather than relying solely on supplements.

 The Conversation
The Conversation
Global Omega-3 Deficiency: Study Reveals Widespread Health Risks and Environmental Impact
A study by Case Western Reserve University indicates a global omega-3 deficiency affecting 85% of the population, due to factors like imbalanced diets high in omega-6 and environmental issues harming marine life. The shortage is linked to increased risks of various health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases and mental health issues, highlighting a need for dietary adjustments and sustainable practices.

 Times of India
Times of India
 The Daily | Case Western Reserve University
The Daily | Case Western Reserve University
 Yahoo News UK
Yahoo News UK
 Ideastream
Ideastream
Mediterranean Diet: Health Benefits, Food Choices, and Bone Health Focus
This article summarizes the benefits, food components, and variations of the Mediterranean diet. It highlights its role in promoting heart and brain health, managing weight, and improving bone density. The synthesis includes expert opinions, specific food recommendations, and lifestyle factors that complement the diet's positive effects. Special attention is given to the diet's impact on bone health and osteoporosis prevention.

 EatingWell
EatingWell
 CNET
CNET
 The Sanford Herald
The Sanford Herald
 LimaOhio.com
LimaOhio.com
Mediterranean Diet: Top 6 Foods for Enhanced Bone Health and Density
The article discusses the importance of the Mediterranean diet for bone health, focusing on six key foods: fatty fish, leafy greens, cheese, tomatoes, prunes, and olive oil. It explains how these foods, rich in nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, potassium, and vitamin K, contribute to bone density and overall bone health. The article further suggests other strategies, including adequate protein intake, limited alcohol consumption, and regular physical activity.

 EatingWell
EatingWell
Natural Ways to Lower Cholesterol: Diet and Lifestyle Changes
The article compiles information on various foods, herbs, and dietary habits that can help lower cholesterol levels. It highlights the importance of incorporating soluble fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and specific nutrients into one's diet to reduce LDL cholesterol and improve overall cardiovascular health. It also mentions the role of lifestyle changes in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.

 EatingWell
EatingWell
 Moneycontrol
Moneycontrol
 Daily Express
Daily Express
 The Economic Times
The Economic Times
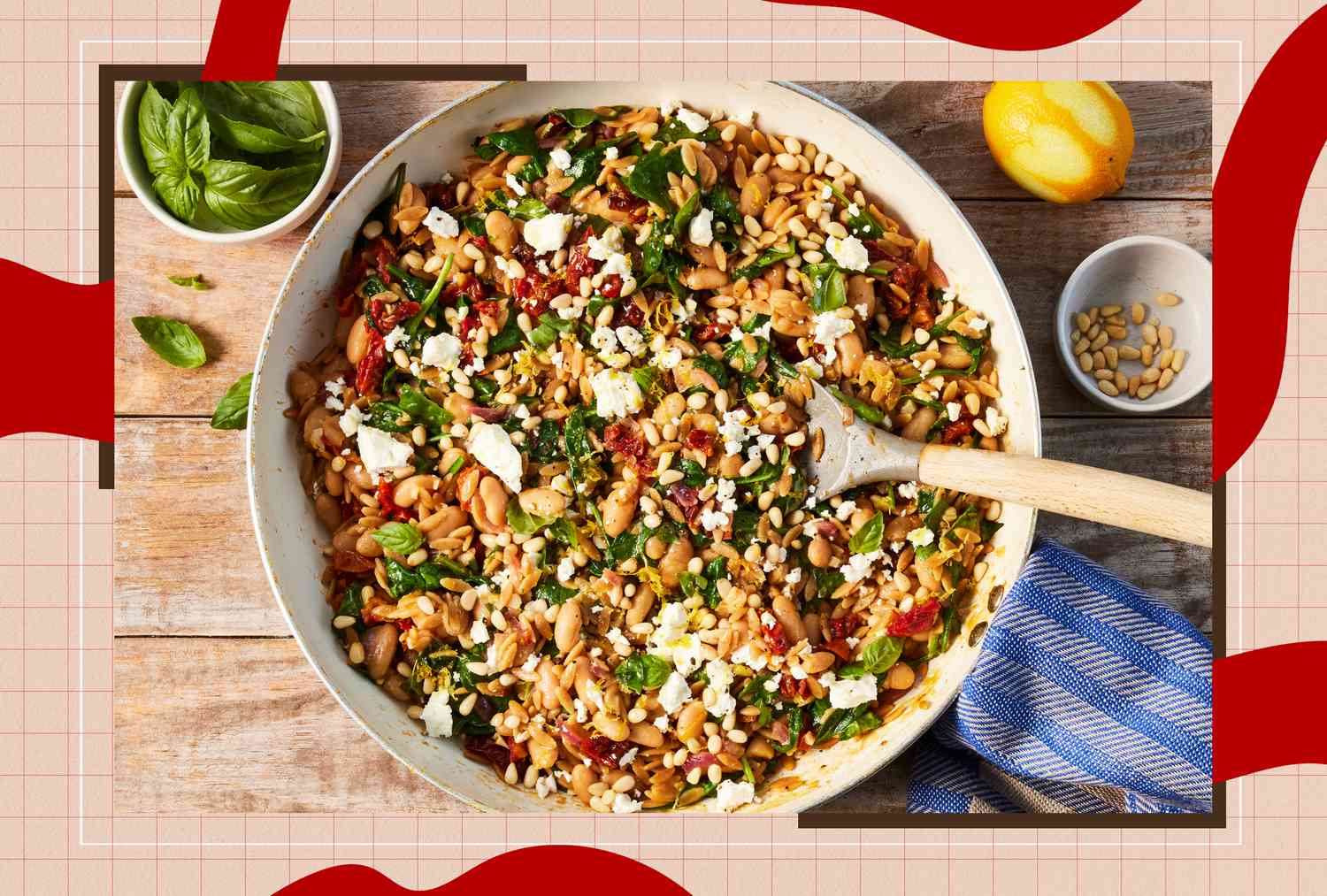
Eating Eggs Regularly May Lower Alzheimer's Risk, Studies Suggest
Recent research indicates that regular egg consumption may be associated with a reduced risk of Alzheimer's disease. The studies highlight the presence of beneficial nutrients in eggs, such as choline, omega-3 fatty acids, and lutein. Findings suggest that including eggs in the diet could potentially mitigate the risk of cognitive decline, particularly for those not already following a Mediterranean diet.

 EatingWell
EatingWell
 Daily Express
Daily Express
 Gloucestershire Live
Gloucestershire Live
 Surrey Live
Surrey Live
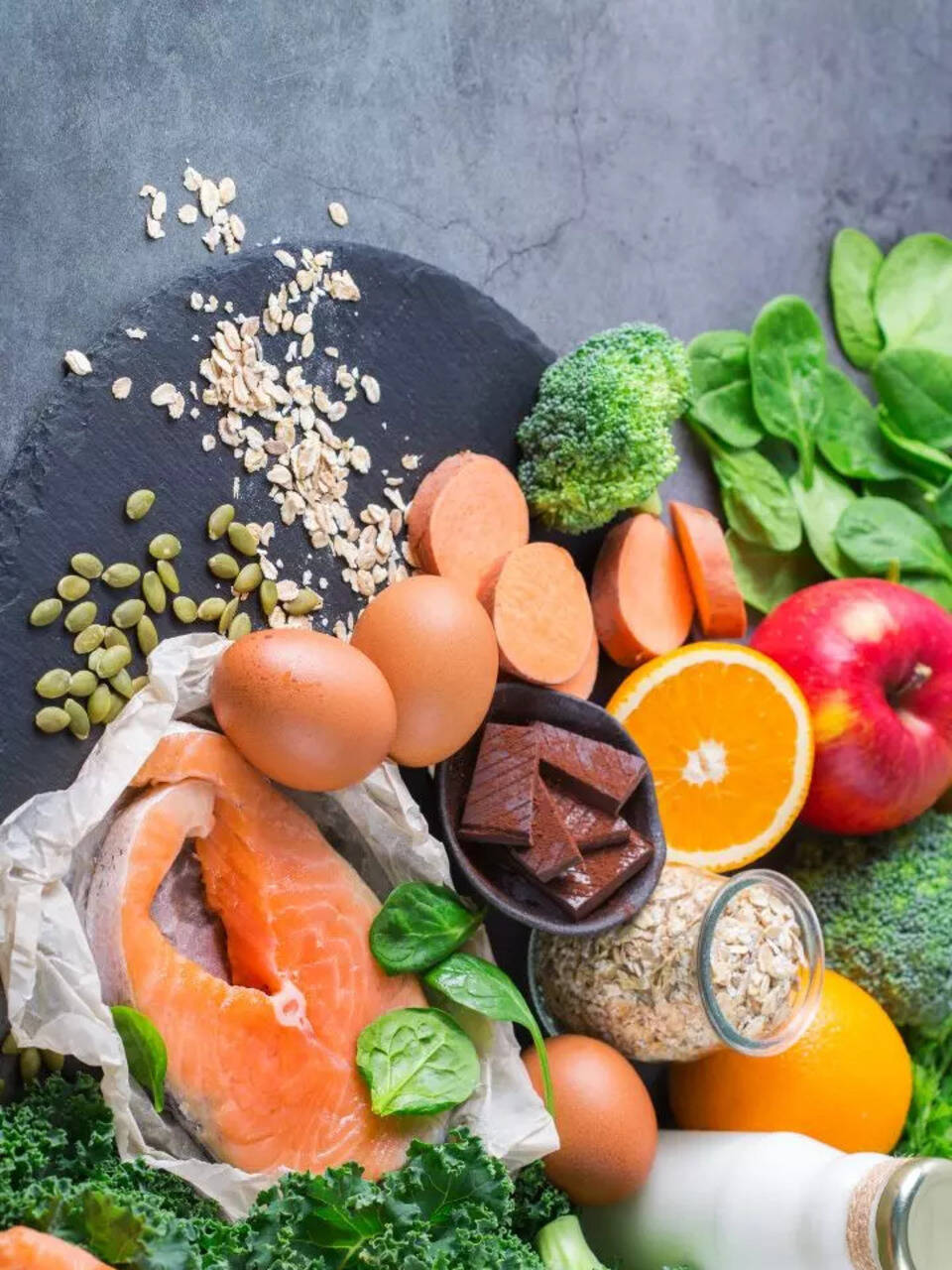
Vitamin D: Sources, Benefits, Deficiency Risks, and Supplementation Advice
This article synthesizes information regarding Vitamin D. It discusses food sources, the benefits of Vitamin D on overall health, what can cause Vitamin D deficiency, what populations are at risk, and expert advice on supplementation, including the best time to take Vitamin D.

 Times of India
Times of India
 Journée Mondiale
Journée Mondiale
 Women's Health
Women's Health
 health.com
health.com
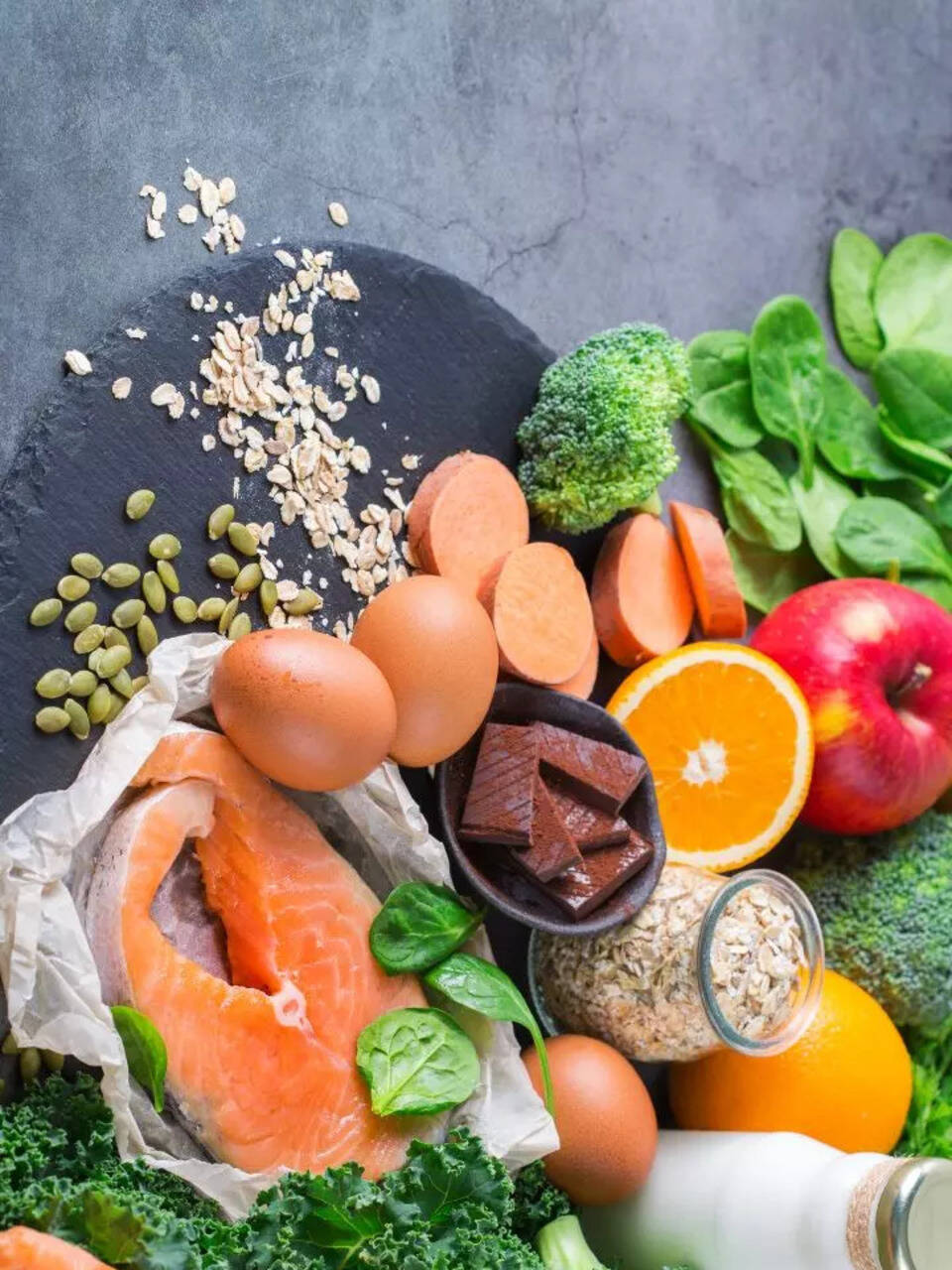
Vitamin D: Benefits, Deficiency Signs, Best Time to Take Supplements, and Food Sources
The article provides a comprehensive overview of vitamin D, highlighting its benefits, deficiency symptoms (particularly in females), dietary sources, and optimal timing for supplementation. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining adequate vitamin D levels for overall health, including bone health, immune function, and mental well-being. It also discusses the role of vitamin D in preventing chronic diseases.

 Times of India
Times of India
 The Indian Express
The Indian Express
 Women's Health
Women's Health
 News18
News18
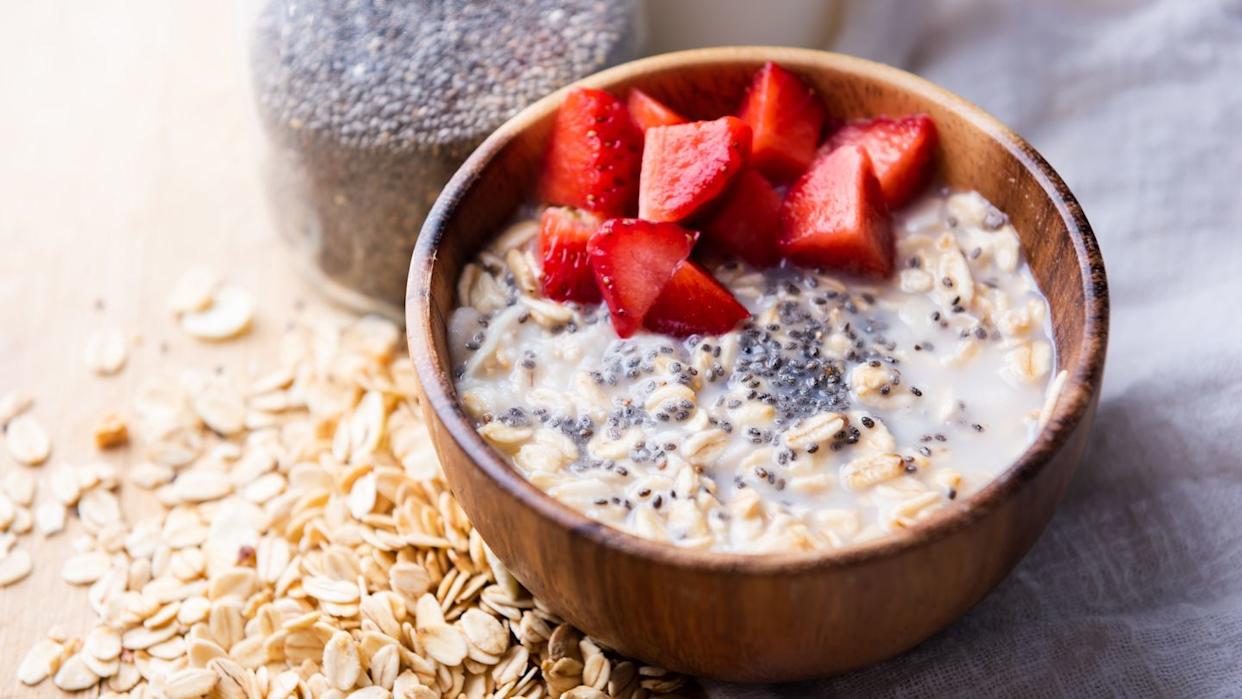
Chia Seeds: Nutritional Powerhouse Linked to Weight Loss, Lower Blood Pressure
This article explores the health benefits of chia seeds based on a recent study analyzing data from 14 clinical trials. It highlights their potential to lower cholesterol and blood pressure, aid in weight management, and provide essential nutrients like fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants. The article also offers practical advice on incorporating chia seeds into your diet and potential risks.

 Yahoo
Yahoo
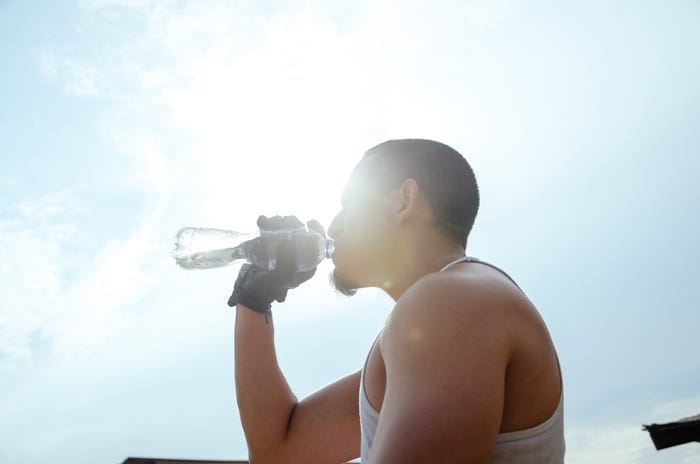
Elite Athletes' Hydration Strategy: Curb Water Intake After 4 PM, Says Nutritionist
Matt Jones, a sports nutritionist, advises elite athletes, including the Boston Celtics, on optimal hydration strategies. Key recommendations include drinking most fluids before 4 p.m. to avoid sleep disruption, monitoring dehydration signs like thirst, weight changes, and urine color, and prioritizing hydrating foods with electrolytes. He emphasizes consistent hydration for improved performance.

 Business Insider
Business Insider
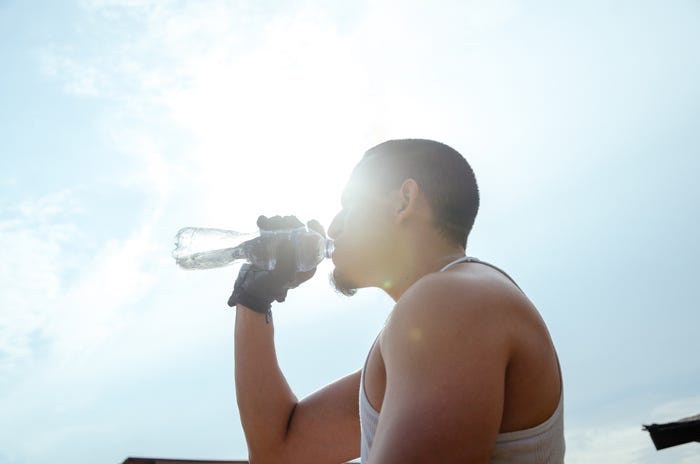
Elite Athletes' Hydration Secrets: Timing and Electrolytes for Peak Performance
This article summarizes advice from a sports nutritionist on how athletes can optimize hydration for better performance, focus, and recovery. It highlights the importance of timing water intake, focusing on electrolytes from foods, and recognizing signs of dehydration. The key is to consume most fluids before 4 p.m. and prioritize potassium-rich foods.

 businessinsider.com
businessinsider.com
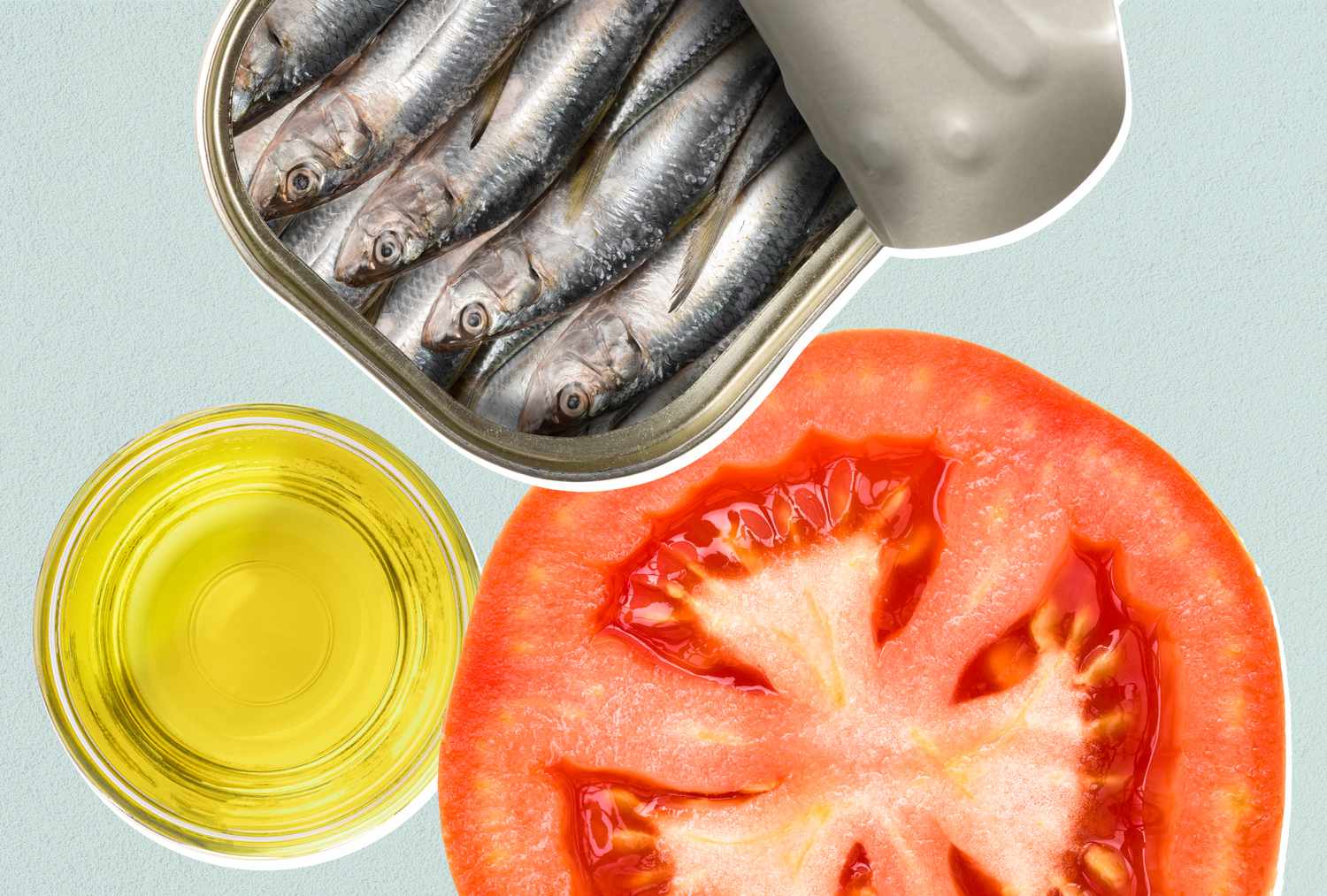
Best Canned Foods for a Mediterranean Diet: Dietitian-Approved, Affordable Choices
This article discusses how canned foods can be a convenient and affordable way to adhere to the Mediterranean diet. It details six specific canned foods, including chickpeas, tomatoes, sardines, artichokes, olives, and white beans, explaining their nutritional benefits and how to incorporate them into meals. It also offers tips for selecting canned foods, such as choosing low-sodium options and reading ingredient lists.

 EatingWell
EatingWell
Best Canned Foods for Mediterranean Diet: Dietitian-Approved, Convenient and Affordable
This article highlights the benefits of using canned foods as part of a Mediterranean diet. It details six recommended canned foods—chickpeas, tomatoes, sardines, artichokes, olives, and white beans—explaining their nutritional benefits and how to incorporate them into meals. It also provides tips for selecting canned goods, emphasizing low-sodium options, minimal ingredients, and olive oil-based products.

 EatingWell
EatingWell
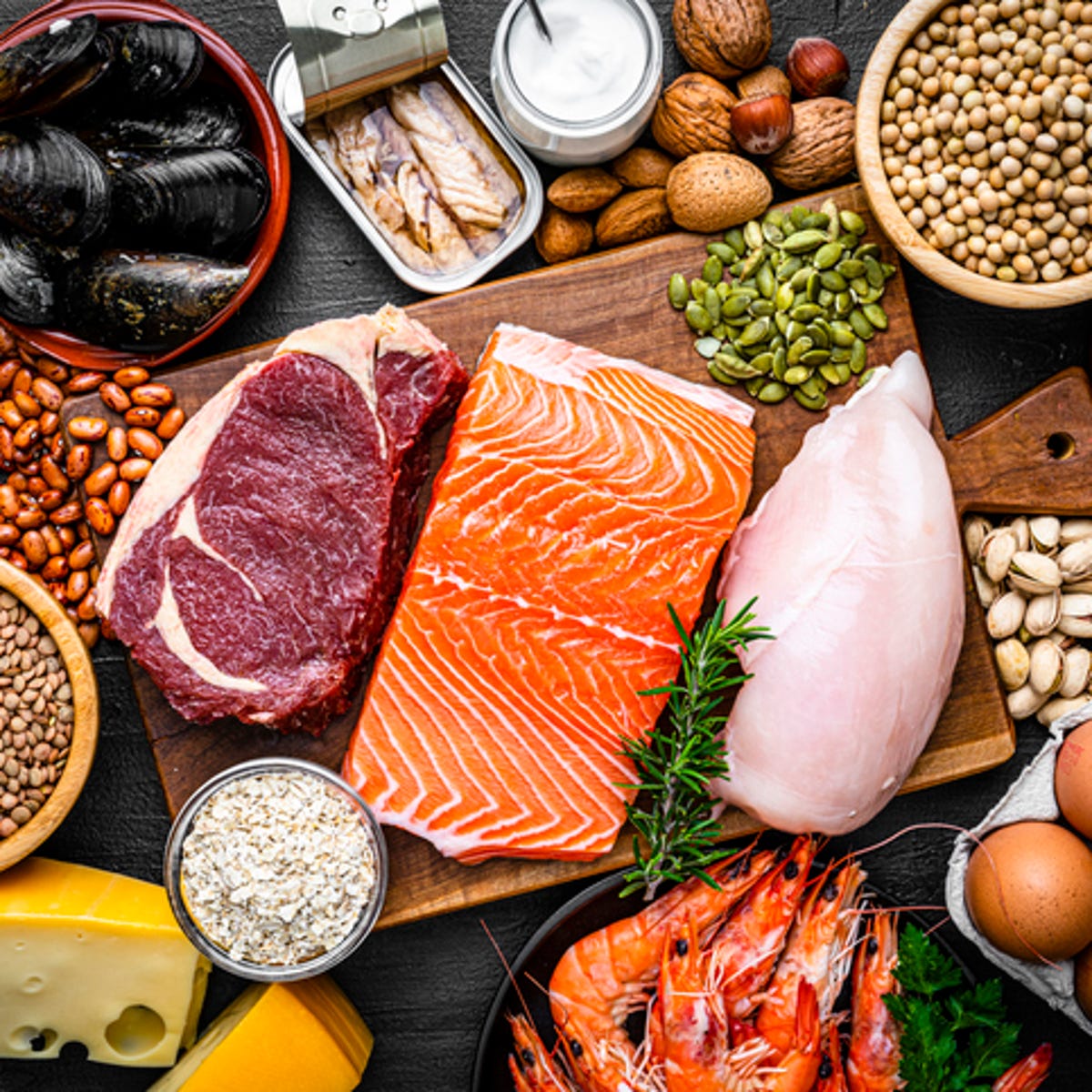
Navigating Protein Needs: Separating Fact from Fiction for Optimal Health
This article synthesizes information on protein intake from various sources, challenging the widespread belief that high protein consumption is universally beneficial. It examines optimal protein levels for different lifestyles, including active individuals, vegetarians, vegans, and older adults, while emphasizing the importance of a balanced diet and debunking common protein myths.

 Medscape
Medscape
 vox.com
vox.com
 CNET
CNET
 Florida State University News
Florida State University News
Protein Needs: Separating Fact from Fiction in Diet and Muscle Building
This article addresses the widespread misconception regarding excessive protein intake for muscle building and general health. It presents scientific evidence to debunk the 'one gram per pound' rule, offering more realistic and personalized recommendations based on activity level and age. The piece also highlights the importance of plant-based protein and a balanced diet.

 Florida State University News
Florida State University News
 CNET
CNET
 vox.com
vox.com
 Medscape
Medscape
Protein Needs: Separating Fact from Fiction in Diet and Exercise Advice
This article examines the current trend of protein maximalism, particularly in the fitness community, and contrasts it with scientific evidence. It debunks the myth of needing extremely high protein intake to build muscle, provides guidelines for adequate protein consumption based on activity level, and emphasizes the importance of plant-based protein sources. The article also addresses the role of protein in weight loss and overall health.

 Florida State University News
Florida State University News
 vox.com
vox.com
 Medscape
Medscape
 CNET
CNET
Western Diet Impairs Gut Microbiome Recovery After Antibiotics, Increasing Infection Risk
A recent study on mice reveals that a diet high in processed foods, red meat, and sugar (Western diet) impairs the gut microbiome's recovery following antibiotic treatment, unlike a fiber-rich diet that promotes rapid restoration. This compromised recovery increases vulnerability to infections like Salmonella, suggesting dietary interventions could be crucial for rebuilding gut microbiota post-medical treatments.

 Earth.com
Earth.com
 Nature
Nature
 Neuroscience News
Neuroscience News
 SciTechDaily
SciTechDaily
Western Diet Hinders Gut Microbiome Recovery After Antibiotics, Diet Key to Restoration
Research indicates that a Western diet, high in processed foods and low in fiber, hinders the recovery of gut microbiome diversity after antibiotic use. Mice fed a Western diet struggled to regain microbial balance and were more susceptible to infections. A diet rich in plant-based fiber aided in faster recovery, suggesting dietary intervention is crucial for gut health.

 Earth.com
Earth.com
 Nature
Nature
 Medical Xpress
Medical Xpress
 Stanford Report
Stanford Report
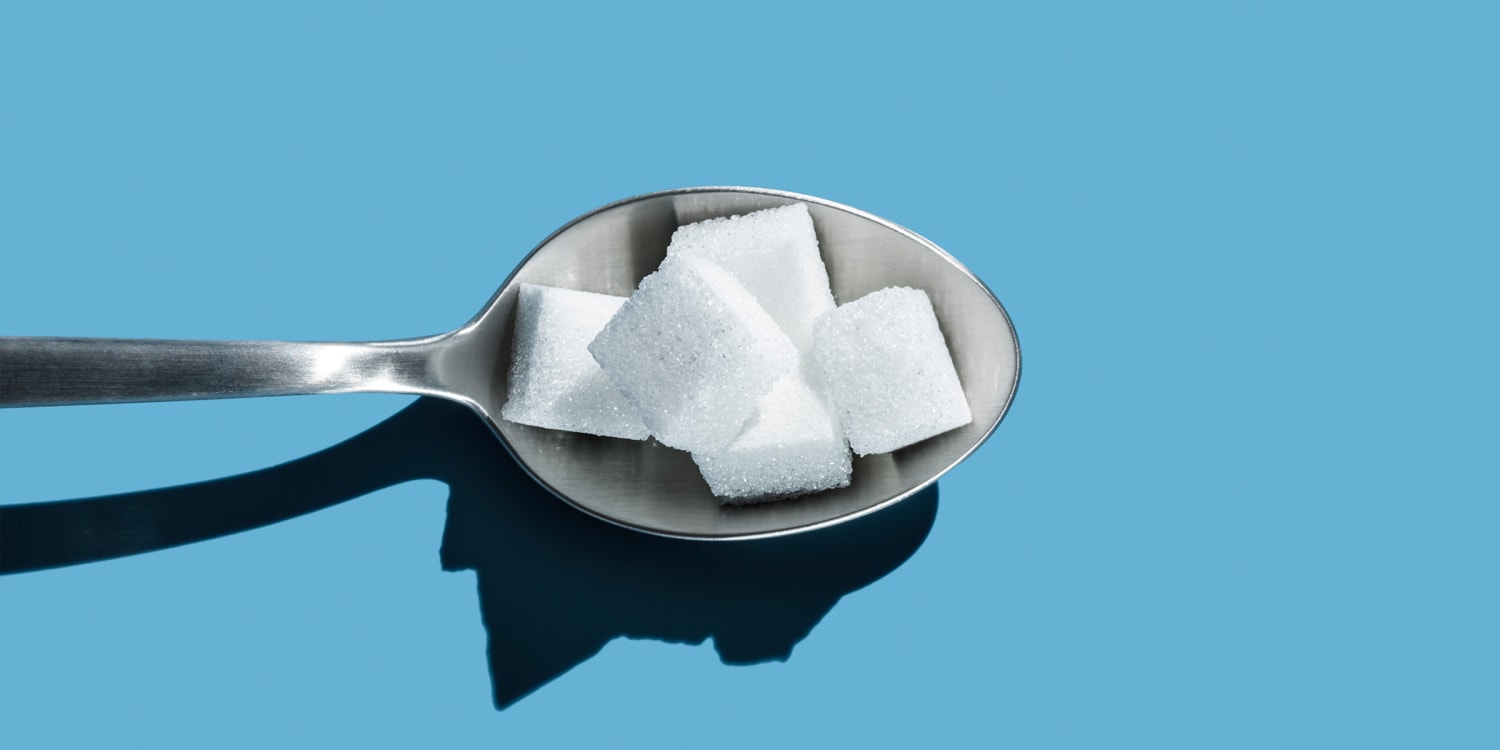
Hidden Sugars: Everyday Foods, Health Risks, and How to Reduce Your Intake
This article discusses the dangers of consuming too much sugar, focusing on the prevalence of hidden sugars in common foods and drinks. It highlights the health risks associated with high sugar intake, including increased risk of dementia, heart disease, and tooth decay, while also offering practical advice on how to identify and reduce sugar consumption.

 TODAY.com
TODAY.com
 NDTV Food
NDTV Food
 Daily Express
Daily Express
 The Times
The Times