Earth's Expiration Dates: Supercomputers Predict When Life and Oxygen Will Vanish
Scientists are using advanced computer models to predict when Earth will become uninhabitable. These models consider factors like the sun's increasing brightness and the depletion of oxygen in the atmosphere. Predictions range from one billion years for the end of oxygen-based life to five billion years when the sun expands into a red giant.

 Daily Mail
Daily Mail
 Yahoo
Yahoo
 IFLScience
IFLScience
 BBC Sky at Night Magazine
BBC Sky at Night Magazine
Physicists Observe Terrell-Penrose Effect, Confirming Einstein's Relativity with Light Speed Illusions
Researchers at TU Wien and the University of Vienna have experimentally demonstrated the Terrell-Penrose effect, an optical illusion where objects moving near the speed of light appear rotated rather than contracted. Using high-speed cameras and laser pulses, they simulated relativistic motion, confirming Einstein's theory and providing visual evidence of this previously unobserved phenomenon. The research offers new insights into relativistic mechanics.

 SciTechDaily
SciTechDaily
 Nature
Nature
 The Debrief
The Debrief
 Phys.org
Phys.org
Soviet-Era Kosmos 482 Crashes to Earth After 53 Years in Orbit
The Soviet-era spacecraft Kosmos 482, intended for a Venus landing, re-entered Earth's atmosphere after 53 years in orbit due to a failed launch in 1972. The re-entry occurred on May 10, 2025, with potential impact locations ranging from the Indian Ocean to the South Asian mainland. The event highlights concerns about space debris and the need for safer spacecraft disposal methods.
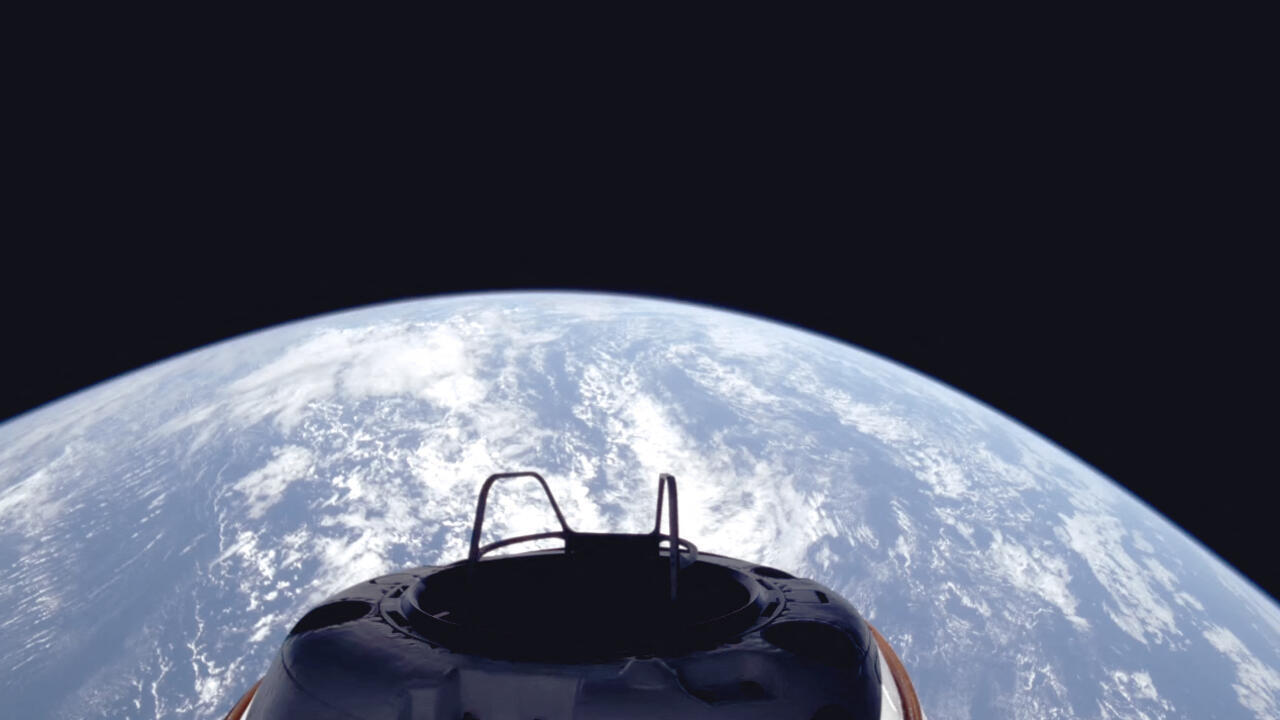

 France 24
France 24
 BBC
BBC
 Space
Space
 The New York Times
The New York Times
Antarctic Glacier Caught in Act of 'Ice Piracy,' Stealing Ice From Neighbor
A recent study utilizing satellite data revealed a phenomenon called 'ice piracy' in West Antarctica, where the Kohler East Glacier is rapidly stealing ice from the Kohler West Glacier. This process, occurring much faster than previously believed, impacts ice sheet stability and sea-level rise projections. The study highlights the crucial role of satellite technology in monitoring and understanding glacial dynamics.
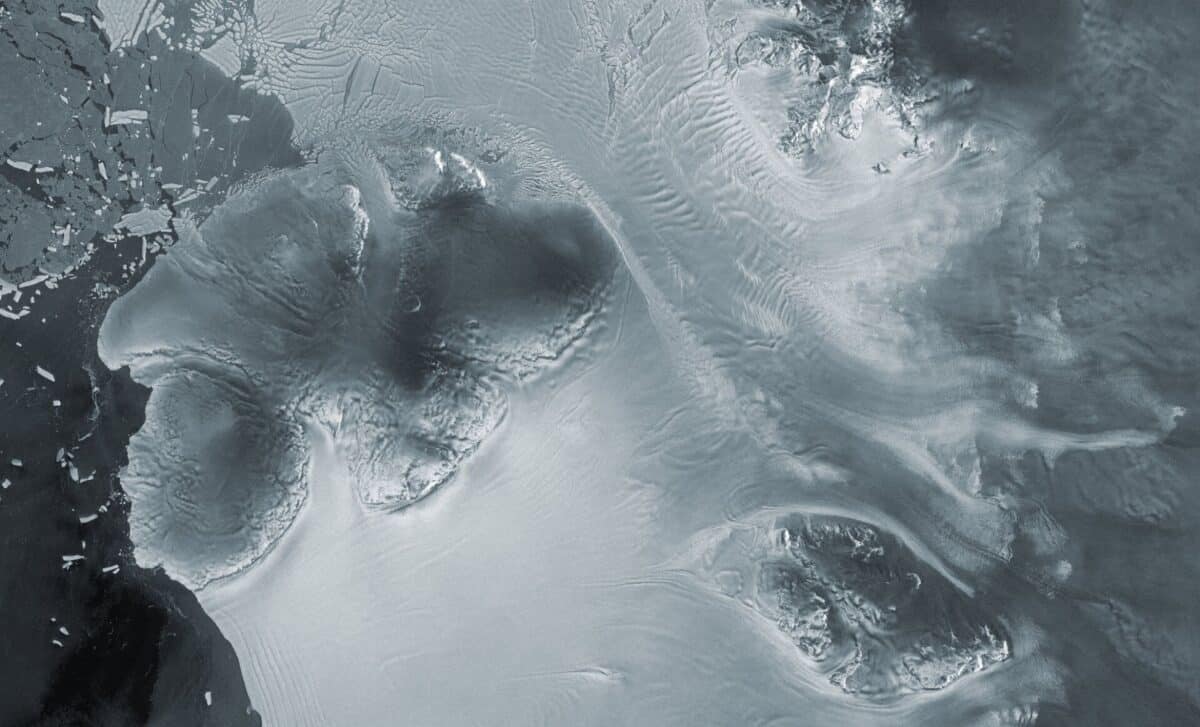

 The Daily Galaxy
The Daily Galaxy
 European Space Agency
European Space Agency
 Phys.org
Phys.org
 Yahoo
Yahoo
Wandering Black Hole Discovered Devouring Star 600 Million Light-Years Away
Astronomers have identified a wandering supermassive black hole, named AT2024tvd, located 600 million light-years away. This black hole is unique as it resides far from its host galaxy's center and was observed consuming a star in a tidal disruption event. The discovery challenges existing theories and opens new avenues for black hole research.
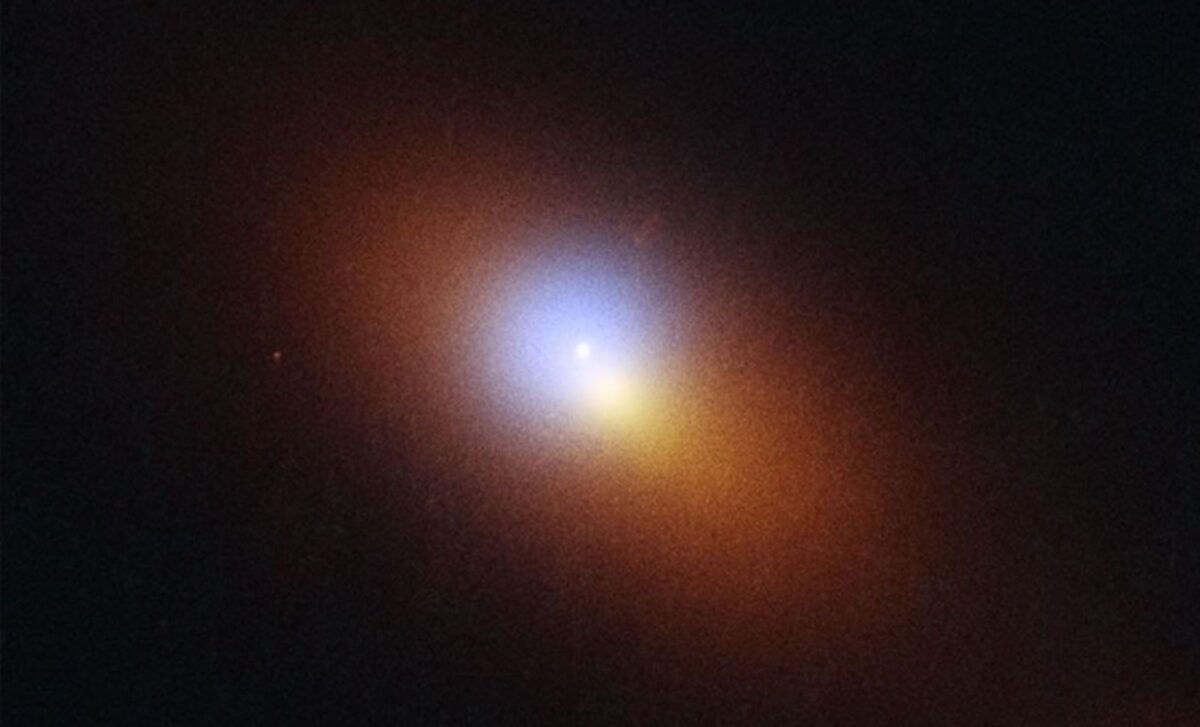

 The Daily Galaxy
The Daily Galaxy
 Space
Space
 Berkeley News
Berkeley News
 Sci.News
Sci.News
Gannon Storm Anniversary: Lessons Learned from the Most Intense Solar Storm in Decades
This article summarizes the impact of the Gannon Storm of May 2024, the most intense solar storm in decades. It details the disruption to GPS systems impacting agriculture, rerouted transatlantic flights, and stunning auroras. The article also highlights NASA's ongoing research and improved space weather awareness due to this event.
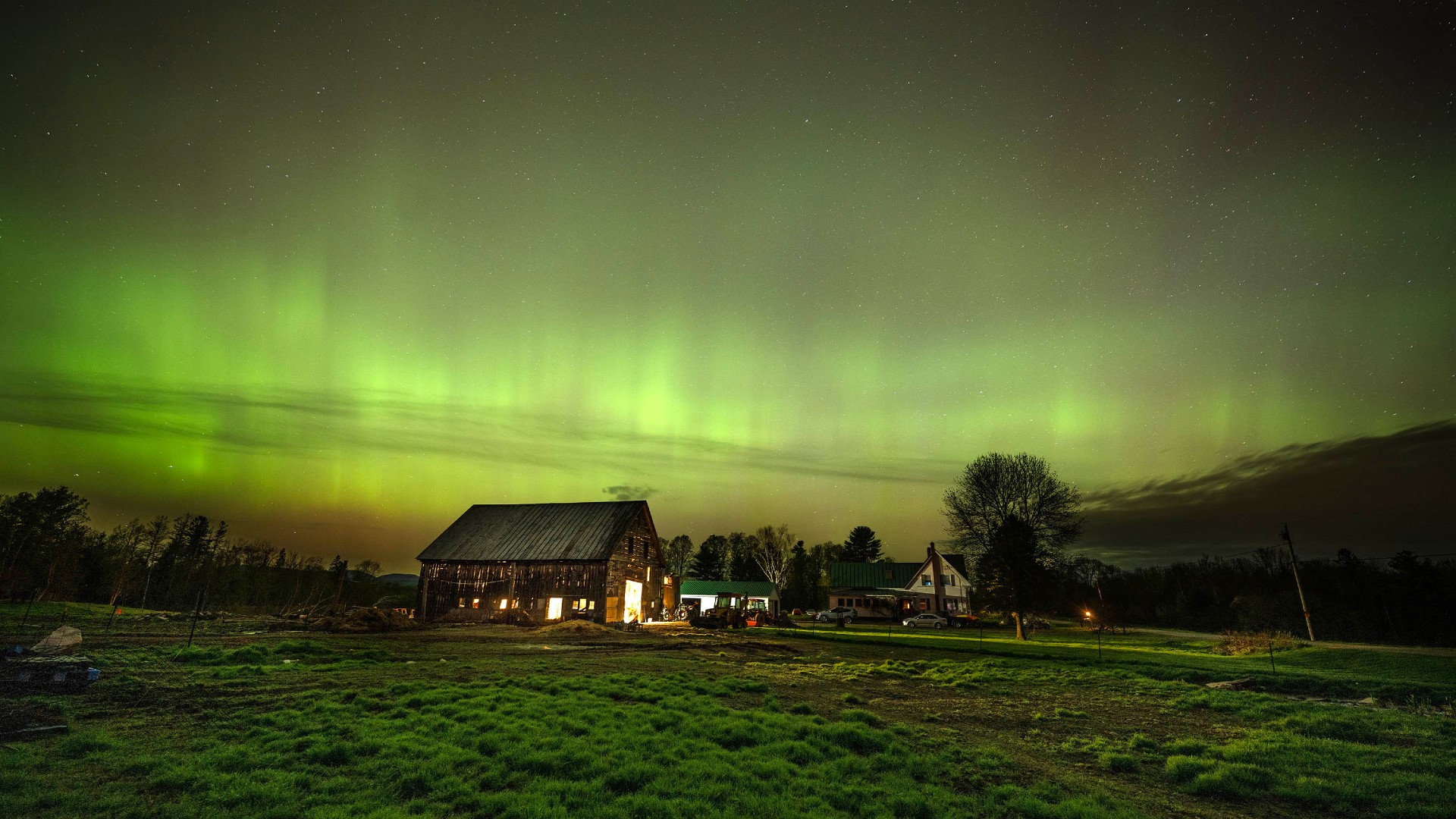

 Space
Space
 NASA Science (.gov)
NASA Science (.gov)
 WGME
WGME
 The Daily Galaxy
The Daily Galaxy
SpaceX Launches Multiple Starlink Missions in Rapid Succession
SpaceX has been actively expanding its Starlink constellation with multiple launches in quick succession. These missions deployed batches of Starlink satellites into low Earth orbit from both Vandenberg Space Force Base in California and Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The launches contribute to the growing Starlink network, which aims to provide global internet service.

 Space
Space
 Florida Today
Florida Today
 Spaceflight Now
Spaceflight Now
 Noozhawk
Noozhawk
Underwater Volcano off Oregon Coast Poised for Potential Eruption: Axial Seamount
Axial Seamount, the most active volcano in the Pacific Northwest, is exhibiting signs of a potential eruption. Scientists are closely monitoring increased seismic activity and magma inflation. While it poses minimal risk to coastal communities, it presents a unique opportunity to study underwater volcanic processes and refine eruption prediction models. Its well-instrumented nature makes it a prime location for research.

 Daily Express US
Daily Express US
 CNN
CNN
 Earth.com
Earth.com
 IFLScience
IFLScience
NASA Faces Major Budget Cuts, Missions at Risk, Artemis Uncertainty Looms
The White House has proposed significant budget cuts to NASA, potentially impacting numerous missions including Mars Sample Return, the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, DAVINCI, VERITAS, and TESS. The cuts also cast a shadow over international collaborations such as the Artemis program. The agency is bracing for tough choices as it faces potential workforce reductions and program terminations.

 SpaceNews
SpaceNews
 The New York Times
The New York Times
 The Planetary Society
The Planetary Society
 CNBC
CNBC
Humans Have Only Seen 0.001% of Deep Seafloor, Study Reveals
A recent study shows that humans have visually explored only 0.001% of the deep seafloor, equivalent to the size of Rhode Island. This limited exploration is heavily biased towards the waters near wealthy countries. The deep sea, crucial for climate regulation, remains largely a mystery, raising concerns about potential impacts of activities like deep-sea mining before sufficient research is conducted.

 AOL.com
AOL.com
 NPR
NPR
 Scientific American
Scientific American
 PBS
PBS
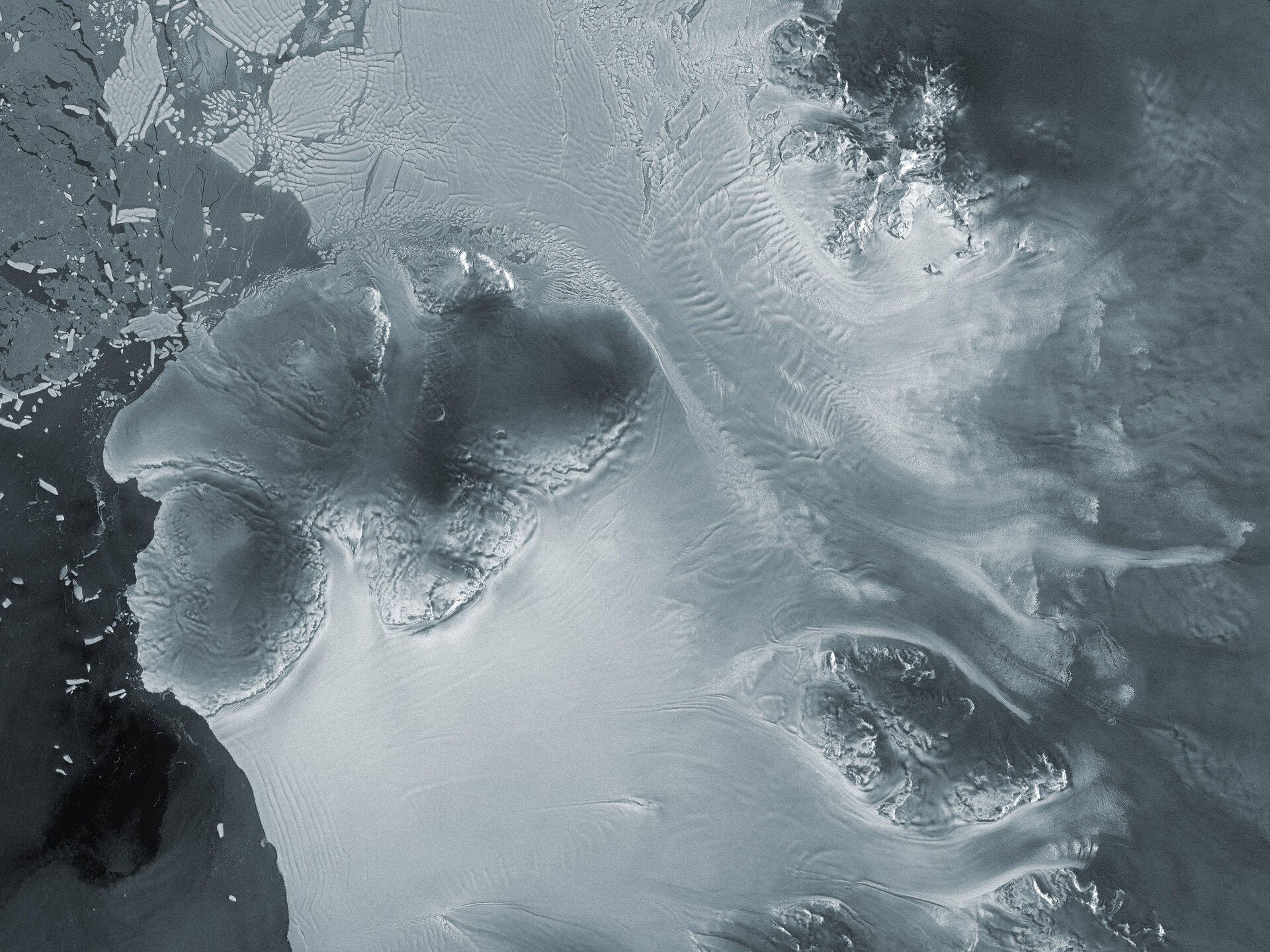
Antarctic Glacier Caught in Act of 'Ice Piracy,' Stealing Ice from Neighbor
A recent study reveals that the Kohler East Glacier in West Antarctica is actively 'stealing' ice from the adjacent Kohler West Glacier. This phenomenon, dubbed 'ice piracy,' is occurring at an unprecedented rate of less than 18 years, challenging previous assumptions about the timescale of glacial dynamics. The change impacts ice flow into the Dotson and Crosson Ice Shelves and contributes to ongoing concerns about sea-level rise.

 European Space Agency
European Space Agency
 Phys.org
Phys.org
 Discover Magazine
Discover Magazine
 British Antarctic Survey
British Antarctic Survey
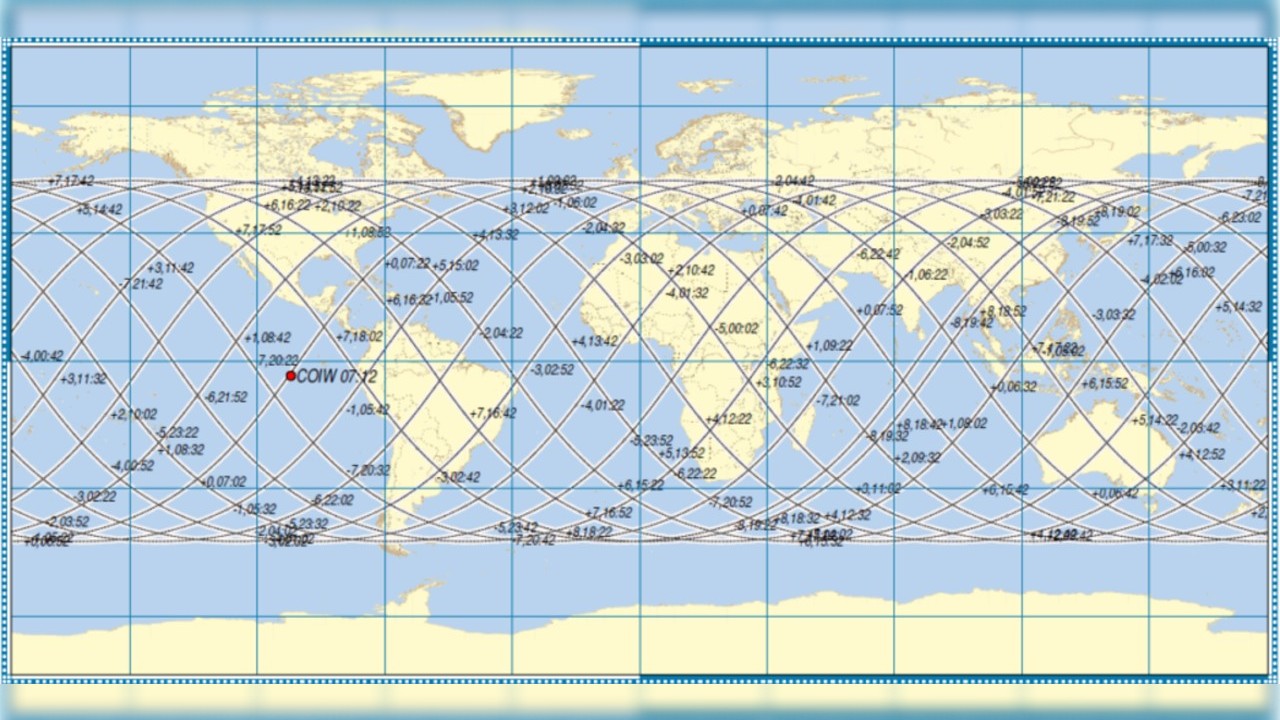
Soviet Kosmos 482 Venus Probe Set to Reenter Earth's Atmosphere After 50 Years
The Kosmos 482 probe, launched by the Soviet Union in 1972 with the aim of reaching Venus, is predicted to reenter Earth's atmosphere. Stranded in orbit due to an engine malfunction, the probe's descent module is expected to fall to Earth around May 10. While the risk of damage or injury is low, experts are closely monitoring the event due to the probe's durable construction.
 Space
Space
 Space
Space
 BBC
BBC
 NPR
NPR
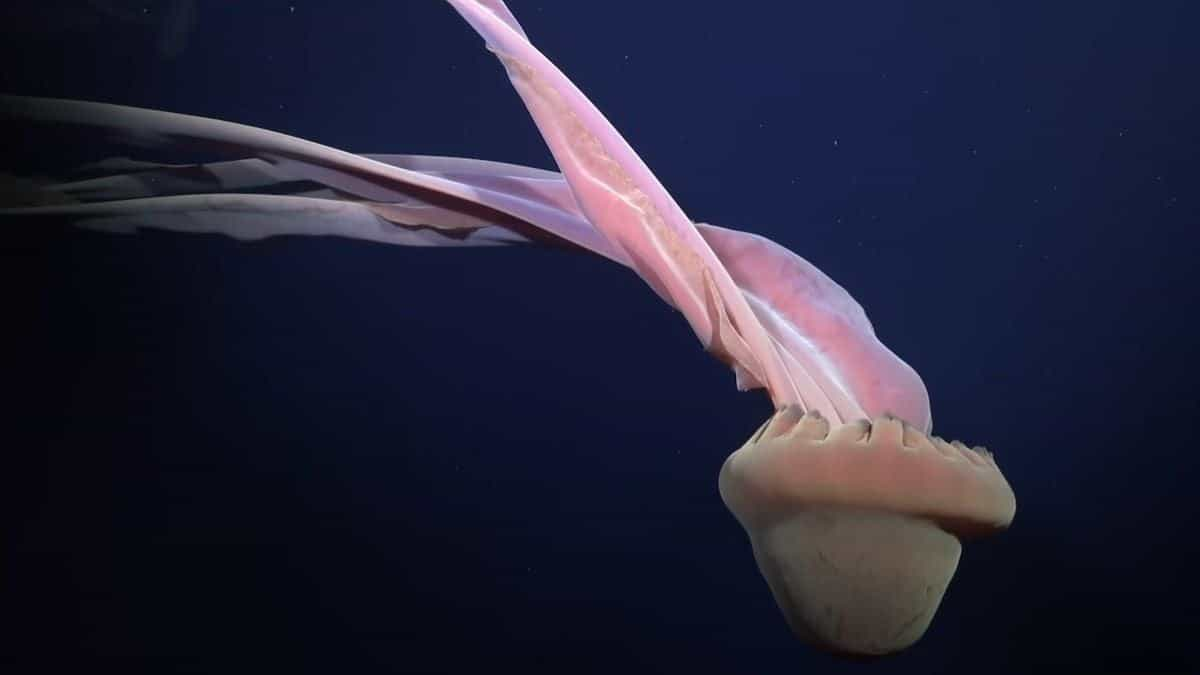
Antarctic Expeditions Reveal Thriving Ecosystems and Rare Marine Life Under Shifting Ice
Recent Antarctic expeditions have revealed thriving deep-sea ecosystems and rare marine life previously hidden beneath ice shelves and glaciers. Scientists have documented unique species, including ghost jellyfish, sea pigs, and colossal squid, while studying the impact of climate change on the region's melting glaciers. These discoveries emphasize the importance of continued Antarctic exploration and conservation efforts.
 Stewartville Star
Stewartville Star
 The Guardian
The Guardian
 The Jerusalem Post
The Jerusalem Post
 Earth.com
Earth.com
Last Universal Common Ancestor (LUCA) Dated to 4.2 Billion Years Ago
A recent study, spearheaded by evolutionary biologists at the University of Bristol, suggests that LUCA, the Last Universal Common Ancestor, existed around 4.2 billion years ago, much earlier than previously thought. This discovery, made using advanced phylogenetic analysis and molecular clock techniques, sheds new light on the origins of life on Earth and the complexity of early ecosystems.

 The Brighter Side of News
The Brighter Side of News
 New Scientist
New Scientist
 Sustainability Times
Sustainability Times
 My Modern Met
My Modern Met
Hubble Tension Deepens: New Coma Cluster Data Challenges Standard Cosmology Model
Recent precise measurements of the Coma Cluster's distance highlight a growing conflict in cosmology. The observed expansion rate of the universe differs significantly from predictions based on the standard Lambda Cold Dark Matter model, derived from cosmic microwave background data. This 'Hubble tension' prompts exploration of alternative models involving dark energy and dark matter interaction.

 SciTechDaily
SciTechDaily
 Astronomy Magazine
Astronomy Magazine
 Big Think
Big Think
 Astronomical Society of Edinburgh
Astronomical Society of Edinburgh
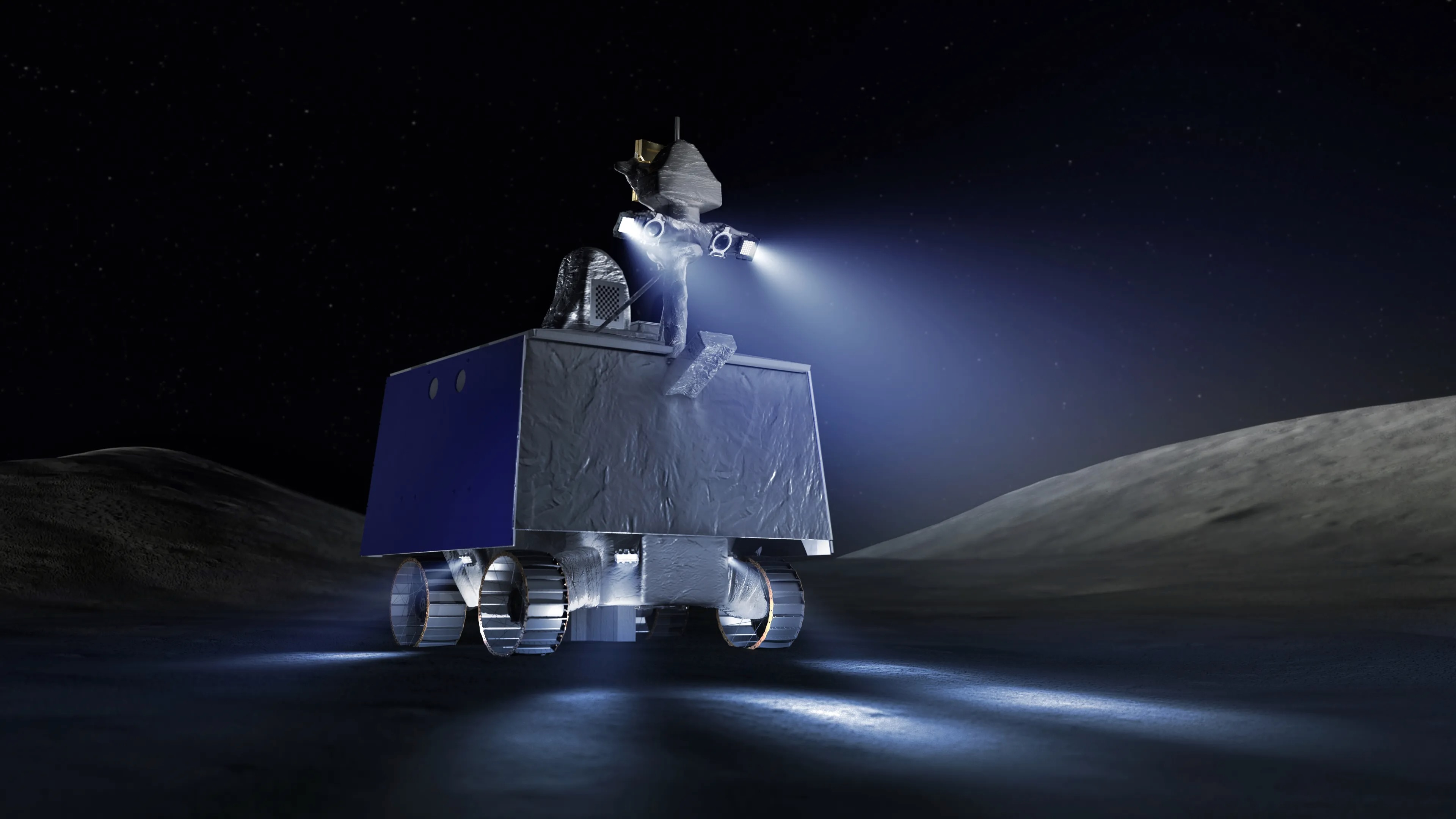
NASA Rethinks VIPER Moon Rover Mission, Cancels Commercial Partnership Plan
NASA has canceled its plans to partner with a commercial entity to send the VIPER rover to the Moon's south pole, reversing course after initially seeking industry proposals. This decision follows concerns about the financial viability of the original partnership structure and criticisms regarding NASA's handling of the VIPER mission, which faced previous cancellation due to cost overruns.

 Space
Space
 SpaceNews
SpaceNews
 upi.com
upi.com
Rare Genetic Mutation Enables Some to Thrive on Just 4 Hours of Sleep
A newly identified genetic mutation, SIK3-N783Y, allows certain individuals to thrive on significantly less sleep (4-6 hours). Research on humans and mice indicates that this mutation affects the SIK3 protein's function, impacting the sleep-wake cycle. The discovery may lead to new treatments for sleep disorders by improving sleep efficiency.

 Live Science
Live Science
 ScienceAlert
ScienceAlert
 Medical Xpress
Medical Xpress
 Yahoo News Canada
Yahoo News Canada
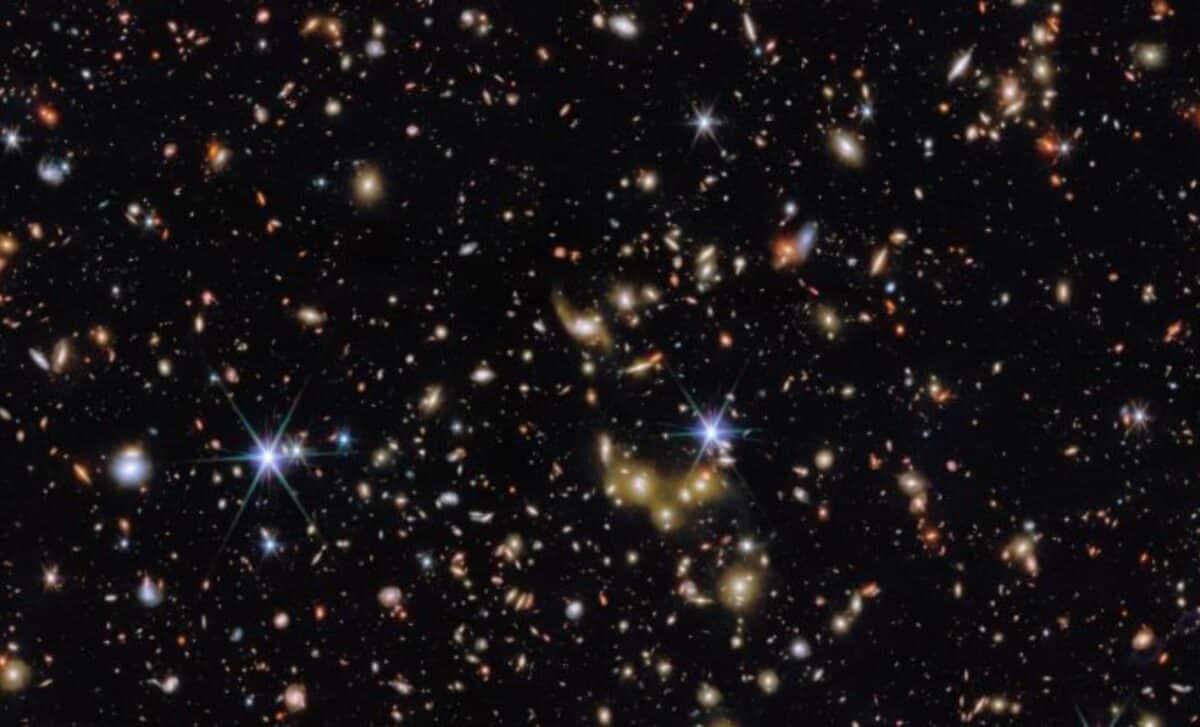
JWST's COSMOS-Web Survey Reveals Thousands of Early Universe Galaxies
The James Webb Space Telescope's COSMOS-Web survey has produced a groundbreaking image revealing thousands of galaxies from the early universe. This survey maps a large area of the sky, providing insights into galaxy evolution, the cosmic web, and the distribution of dark matter. The image contains galaxy groups from as far back as 12 billion light-years, offering a glimpse into the universe's formative years.

 The Daily Galaxy
The Daily Galaxy
 Big Think
Big Think
 Live Science
Live Science
 New Scientist
New Scientist
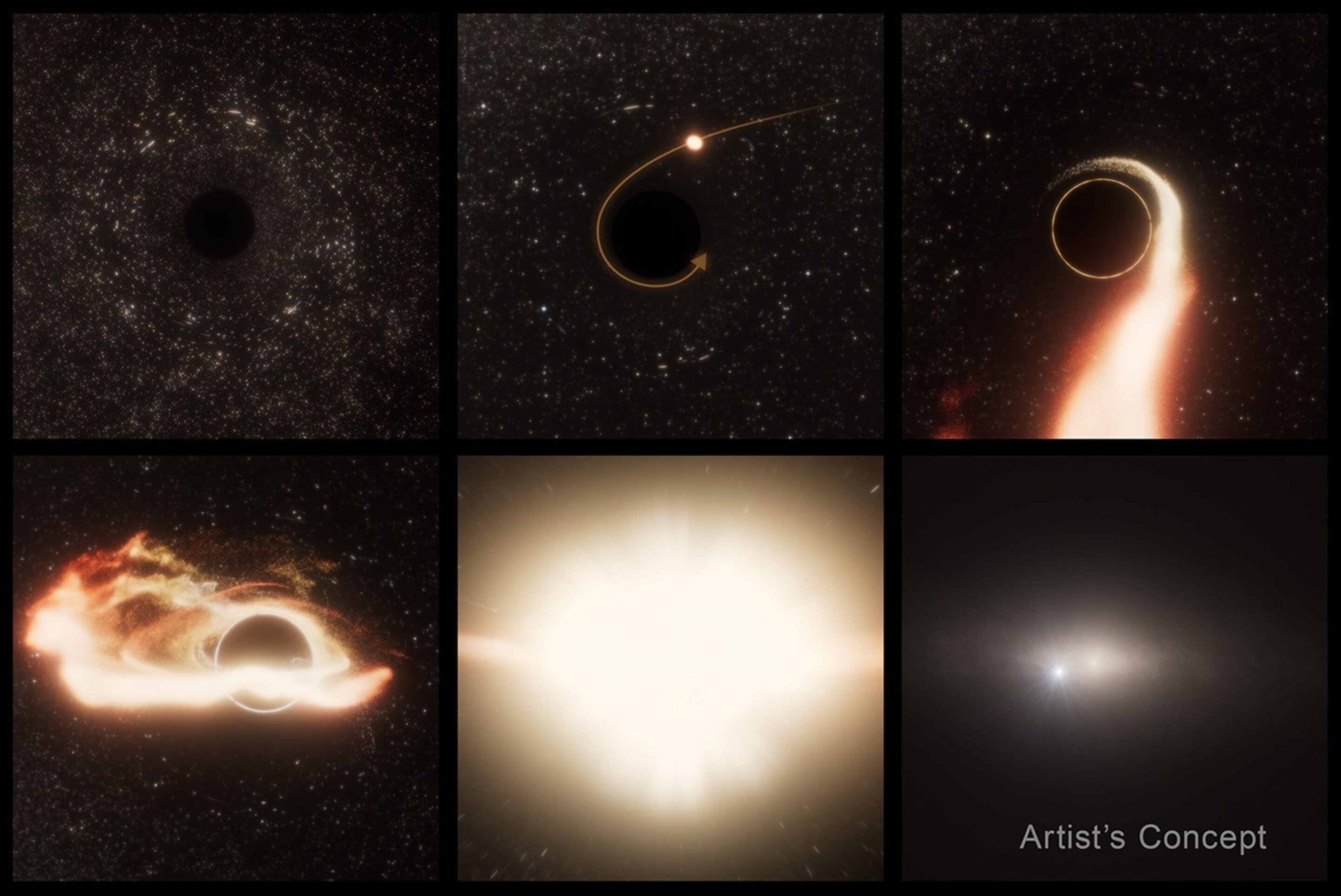
Wandering Black Hole Discovered Shredding Star 600 Million Light-Years Away
Astronomers have identified a wandering supermassive black hole, located 600 million light-years away, through the observation of a tidal disruption event (TDE) named AT2024tvd. This black hole, unlike others typically found at the center of galaxies, is offset and was discovered as it consumed a star, emitting a burst of radiation. The discovery has implications for understanding the behavior and origin of black holes.

 Phys.org
Phys.org
 NASA Science (.gov)
NASA Science (.gov)
 NDTV
NDTV
 Sci.News
Sci.News
Sun's Filament Eruptions Send Solar Energy Waves; Earth Dodges Direct Impact
On May 7, 2025, the Sun unleashed a series of solar filament eruptions, producing coronal mass ejections. Fortunately, Earth avoided a direct impact. While some minor geomagnetic storm conditions are possible, experts are monitoring solar activity and advising those sensitive to magnetic changes to take precautions, highlighting the ongoing interplay between solar activity and terrestrial conditions.

 The Daily Galaxy
The Daily Galaxy
 Space
Space
 Evrim Ağacı
Evrim Ağacı
 The Watchers - Watching the world evolve and transform
The Watchers - Watching the world evolve and transform